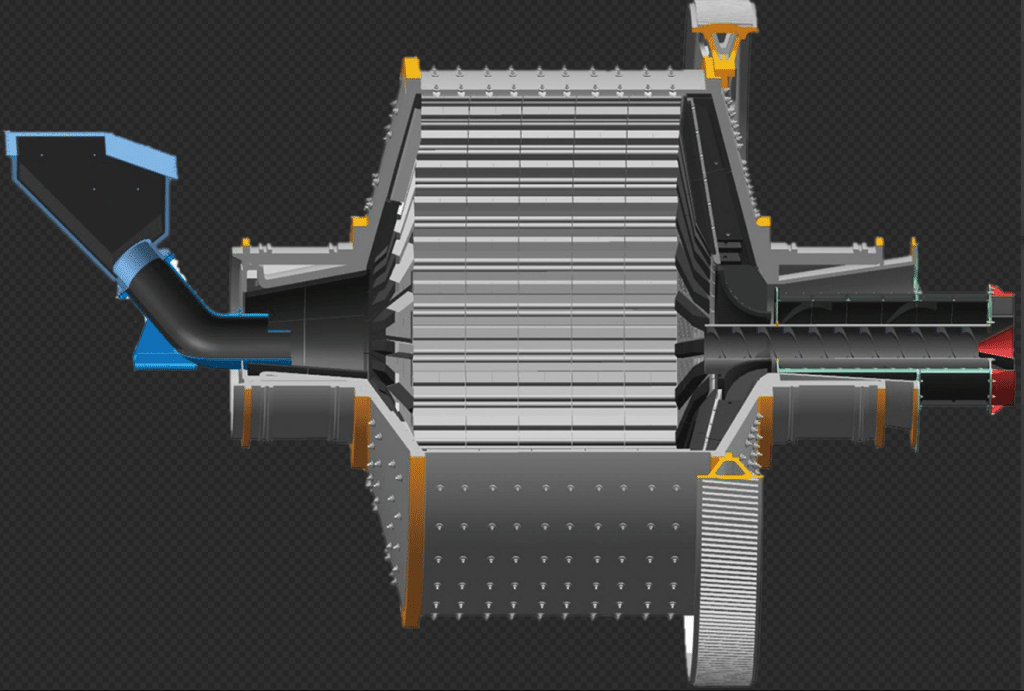
Protective liners serve as a vital component in industrial equipment, particularly in environments exposed to high abrasion, impact, or chemical exposure. Among the various types of protective liners, forged liners are recognized for their mechanical strength and extended durability. Their performance has a direct impact on equipment efficiency, process stability, and long-term maintenance costs.
This article covers the key aspects of forged liners, including their material composition, selection principles, and installation practices, offering practical insights to help improve industrial equipment performance.
Materials of Protective Liners
Choosing the right protective liner material depends on working conditions, material flow characteristics, and long-term maintenance goals.
High-manganese Steel
High-manganese steel is renowned for its exceptional work-hardening capability. Under repeated impact, its surface hardness significantly increases. However, in low-impact or low-wear systems, high-manganese steel may not fully harden, resulting in a shorter effective service life compared to high-impact applications. Therefore, it is particularly well-suited for equipment that endures intense mechanical shock, such as grinding mills and crushers.
Alloy Steel
Forged alloy steel liners are designed to deliver a balance between wear resistance and structural strength. By incorporating elements such as chromium, molybdenum, or nickel, these protective liners can be tailored to meet specific load and abrasion requirements. This makes them particularly useful in applications that demand both high strength and moderate to high wear resistance. In mining mills, alloy steel liners are commonly applied into the grinding chamber, as they can withstand the demanding conditions of ore processing.
Stainless Steel
In operations where corrosion is a constant concern, stainless steel delivers a dependable solution. Its resistance to rust, oxidation, and chemical attack makes it a go-to material for handling acidic or moisture-laden environments. While it comes at a higher cost, its stability in harsh conditions leads to longer operational cycles and lower contamination risk.
The materials mentioned above are suitable for forged liners, while other materials can be utilized for different types of protective liners in mining mills:
High-chromium Cast Iron
High-chromium cast iron, with its high hardness, effectively resists wear from ore grinding and is ideal for low-impact, grinding-intensive applications, such as the feed ends of autogenous mills and the liners of ball mill shells. However, its lower toughness makes it inappropriate for high-impact loading conditions.
Rubber
Rubber liners excel at reducing noise, vibration, and surface wear in continuous material flow systems. Composite liners that combine rubber with metal or ceramic backing are employed to balance impact resistance and energy absorption. These liners are particularly effective in slurry handling and screening systems.
Selection Principles of Protective Liners
To select the proper protective liner, a structured evaluation of how the liner will interact with the equipment, process material, and operating environment is essential. Here are the key principles to guide your purchasing decision:
Equipment Type Matching
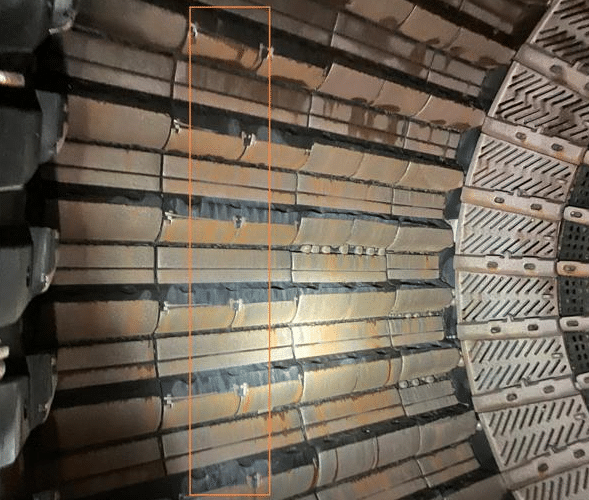
Different equipment operates under varying mechanical conditions, placing distinct demands on protective liners. For example, crushers generate intense impact forces, requiring liners with exceptional resistance to sudden mechanical shock. In contrast, ball mills rely on liners that assist in lifting and cascading the grinding media, which demands careful attention to shape, alignment, and controlled wear. A well-designed ball mill lining supports this process by maintaining optimal media motion and reducing uneven wear inside the mill.
Material Characteristics
Hardness, particle shape, and size directly affect the rate at which a protective liner wears down. Materials with high abrasiveness require harder surfaces, while corrosive substances call for chemical-resistant alloys or stainless steel. Systems processing sticky or fine materials need smoother liners to prevent buildup and maintain flow consistency.
Working Environment Adaptability
Temperature, moisture levels, and chemical exposure vary significantly across industrial environments. Liners installed in high-temperature zones must resist deformation and retain their strength when exposed to heat cycling. In humid or chemically reactive atmospheres, corrosion-resistant materials are critical. Matching the liner’s resistance properties with actual site conditions helps prevent premature failures and unplanned shutdowns.

Economic Consideration
The best protective liner is not always the most expensive or the hardest. Effective selection considers the total cost of ownership, including initial price, installation complexity, expected service life, and frequency of maintenance. A liner that costs more upfront but delivers longer runtime and quicker replacements may provide better long-term value than a lower-priced option that necessitates frequent interventions.
Installation Guidelines for Protective Liners
Accurately installing a protective liner is vital to assuring it performs reliably. Here is a step-by-step guide.
Preparation
Equipment Inspection: The surface of the equipment must be cleaned and checked for damage. Dirt, corrosion, or old adhesive residues can interfere with the contact between the liner and the base surface. Verify that anchoring points, bolt holes, and structural joints are intact. Address any defects before bringing in the new protective liner.
Liner Pretreatment: Inspect each liner to confirm that its dimensions match the design specifications. Look for defects, warping, or inconsistencies. If cutting or drilling is necessary, complete these tasks before positioning the liner. Preparing the protective liner in advance helps avoid delays and reduces the risk of improper fit during installation.
Installation Process
Positioning and Fixing: Align the liners precisely with the equipment layout, following the intended flow direction. Depending on the system, liners may be fixed using bolts, welding, clamps, or other hardware. Care must be taken to maintain consistent spacing and alignment so the liner performs evenly without creating pressure points or flow disturbances.
Fastening and Verification: Once the liner is positioned, all fasteners should be tightened according to specification. It’s important to check for movement or loose fittings that could cause the liner to shift during use. Any misalignments should be corrected before the equipment is restarted. A final inspection ensures all sections are secure, fastened properly, and free of gaps or inconsistencies. If this step is skipped or rushed, it can compromise the entire lining system, even if high-quality materials are used.
Naipu Protective Liners Recommendation
Wear has always been a significant challenge affecting the service life and production efficiency of equipment. To effectively address this issue, Naipu is committed to providing efficient and reliable wear liner solutions through technological innovation and material research.
Naipu GH6 and GH3 forged alloy liners are designed with a scientific and rational composition, featuring fine grain structure, high density, excellent hardenability (maximum hardenable wall thickness: 400 mm), minimal inclusions, and stable microstructure. These characteristics enable them to exhibit exceptional wear resistance under dynamic impact wear conditions.
Specifically, in comparative tests with traditional wear-resistant materials, GH3 demonstrates 42.1% higher wear resistance than 70CrMo steel, while GH6 shows 52.7% higher wear resistance than CrMo steel. This means that under the same working circumstances, GH6 and GH3 forged alloy liners are capable of substantially increasing the equipment’s service life, decreasing the frequency of replacements, and consequently reducing maintenance expenses and downtime, thereby delivering considerable economic advantages to mining operations.
Wrapping Up
Protective liners play a key role in keeping industrial equipment efficient, stable, and protected from wear. Determining the right material, following correct selection principles, and guaranteeing correct installation all contribute to long-term performance. Naipu forged alloy liners present proven wear resistance, structural stability, and reliable service life. For operations that demand durable, high-performance solutions, these liners are a smart and tested choice.