The way audiences consume video content has changed dramatically over the past decade. Traditional broadcasters, digital media companies, and streaming platforms now operate in a fast-paced environment where accessibility, speed, and efficiency are critical. In this context, automatic subtitles have evolved from a nice-to-have feature into a strategic necessity for modern broadcasting.
Viewers today expect content to be available anytime, anywhere, and on any device. They also expect video to be easy to understand, even when sound is unavailable or inconvenient. This shift has forced broadcasters to rethink their production and distribution workflows.
A New Era of Video Consumption
Video is no longer consumed only in front of a television. Audiences watch news, entertainment, and live events on mobile devices, laptops, and tablets, often in public spaces or at work. In many of these situations, audio is muted by default.
Subtitles ensure that content remains understandable and engaging regardless of the viewing environment, making them a core component of modern video strategy.
Accessibility as a Strategic Requirement
Accessibility is one of the strongest arguments for implementing subtitles at scale. Subtitles make video content accessible to deaf and hard-of-hearing audiences and help non-native speakers better understand spoken language.
For broadcasters with international reach, accessibility is no longer optional—it is a fundamental part of responsible and inclusive media distribution.
Automatic Subtitles and Broadcast Workflows
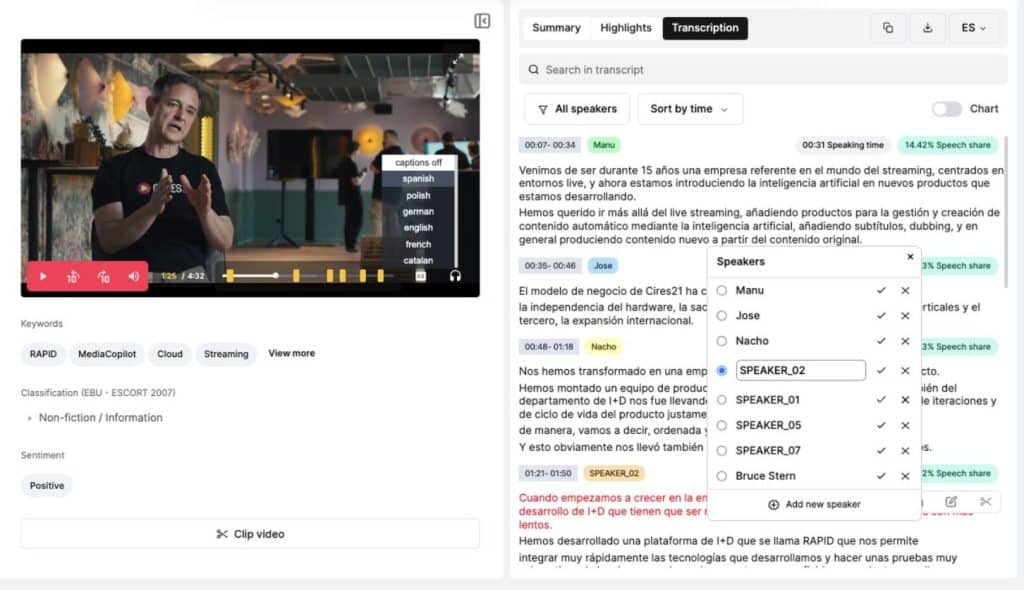
To meet these demands efficiently, many broadcasters are turning to automation. Using an automatic subtitle generator allows media organizations to produce subtitles quickly and consistently across large volumes of content. Instead of relying solely on manual transcription, broadcasters can integrate automated subtitling directly into their production pipelines.
This approach significantly reduces turnaround times, lowers operational costs, and enables faster publishing—especially important for news, live events, and high-frequency programming.
Compliance and Regulatory Considerations
In many regions, broadcasters are legally required to subtitle a portion of their programming. These regulations often apply to news, public service content, and prime-time broadcasts.
Automatic subtitles help broadcasters meet compliance requirements more efficiently, particularly when dealing with live or time-sensitive content. While human review may still be necessary in certain cases, automation provides a scalable foundation.
Real-Time Subtitles for Live Broadcasting
One of the most impactful applications of automatic subtitles is in live broadcasting. Advances in speech recognition and artificial intelligence now make it possible to generate subtitles in near real time.
For live news, sports, and events, this means:
- Improved accessibility for live audiences
- Reduced reliance on specialized stenography teams
- Faster response to breaking news situations
Although real-time subtitling presents technical challenges, accuracy continues to improve as AI models evolve.
Enhancing the Viewer Experience
Subtitles improve more than just accessibility—they enhance the overall viewer experience. They help audiences follow complex discussions, understand unfamiliar accents, and stay engaged during long-form content.
For digital platforms operated by broadcasters, subtitles also contribute to higher watch times and better audience retention, both critical performance metrics.
Content Reuse and Editorial Efficiency
Automatic subtitles generate structured text data that can be reused across editorial workflows. Transcripts can support:
- Content indexing and archiving
- Searchable video libraries
- Clip creation and highlights
- Editorial research and documentation
This added value makes subtitles a resource not only for viewers but also for internal teams.
Multiplatform Distribution Made Easier
Modern broadcasters distribute content across multiple channels: traditional TV, websites, mobile apps, social media, and OTT platforms. Each channel has different technical and accessibility requirements.
Automatic subtitles simplify this process by enabling faster adaptation of content to multiple platforms without duplicating production efforts.
AI Technology Behind Automatic Subtitles
Automatic subtitle generation relies on speech-to-text and natural language processing technologies. These systems analyze audio signals, identify speech patterns, and convert spoken language into synchronized text.
As artificial intelligence continues to advance, subtitle accuracy, language support, and real-time performance continue to improve—making automated solutions increasingly reliable for professional broadcast use.
Best Practices for Broadcasters
To get the most value from automatic subtitles, broadcasters should:
- Implement quality control for high-impact content
- Customize vocabularies for proper names and technical terms
- Combine automation with editorial oversight
- Continuously evaluate accuracy and performance
Automation works best when it complements, rather than replaces, editorial expertise.
The Future of Automatic Subtitles in Broadcasting
The future of broadcasting will be increasingly automated, data-driven, and accessible. Automatic subtitles will play a central role in this transformation, supporting faster production, broader reach, and more inclusive content.
As audiences continue to demand flexibility and accessibility, automatic subtitling will become a standard component of professional broadcast operations.
Conclusion
For broadcasters, automatic subtitles are no longer just a technical feature—they are a strategic asset. They improve accessibility, streamline workflows, support compliance, and enhance the viewer experience across platforms.
By integrating automatic subtitling technologies such as an automatic subtitle generator, broadcasters can future-proof their operations and meet the evolving expectations of modern audiences.