Forex, like any other financial market, is subject to analysis. Traders use various analysis methods to predict future price movements and make the right investment decisions. Let’s explore the two main approaches to Forex market analysis:
Technical Analysis
Technical analysis is based on the study of historical price data. It operates on the principle that the market “remembers everything” and that history tends to repeat itself. Traders who use technical analysis rely on price charts, indicators, and patterns to forecast future price movements.
Technical analysis encompasses a range of tools and methods to study market price movements. The most popular methods of technical analysis include:
Chart Analysis
- Line Charts: Constructed using the closing prices for each time period.
- Candlestick Charts: Display the opening, closing, high, and low prices for a specific period.
- Bar Charts: Similar to candlestick charts but represented as vertical bars.
Trend Indicators
- Moving Averages (MA): Help determine the trend direction.
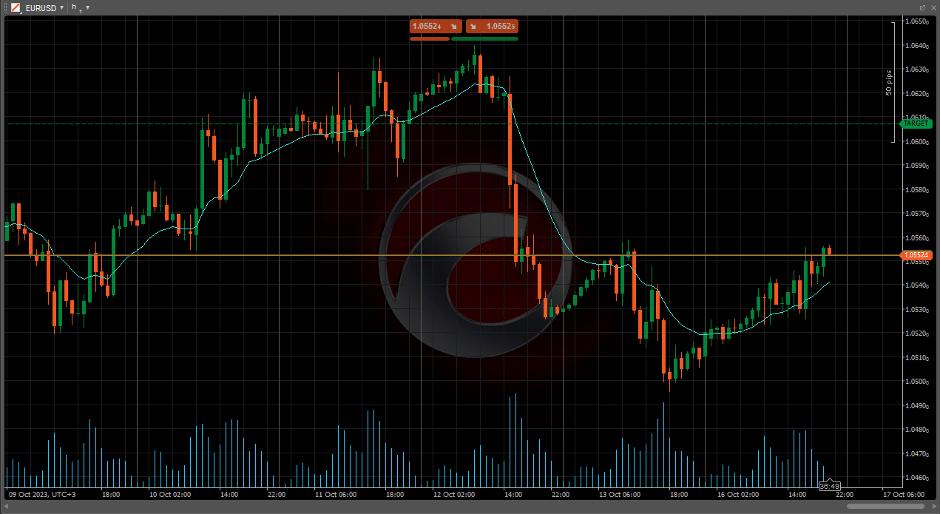
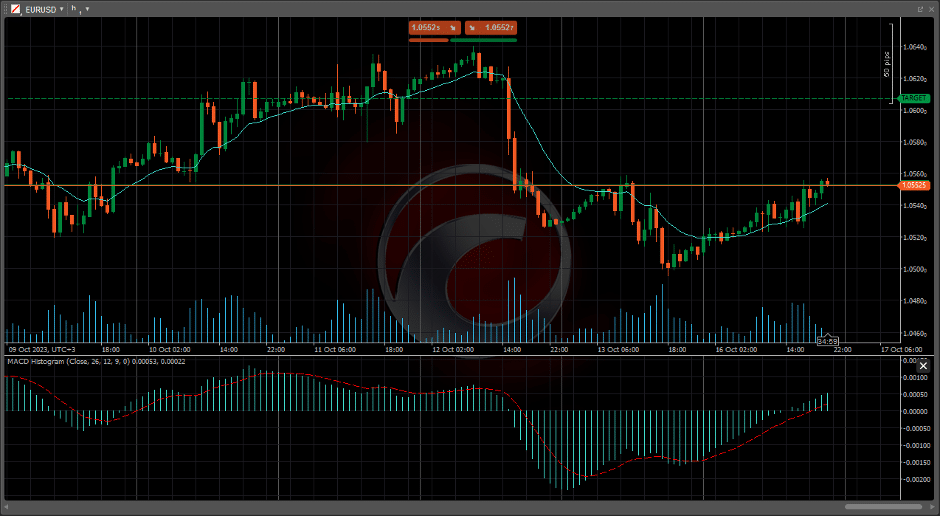
- MACD: Shows the difference between two moving averages.
- Parabolic SAR System: Consists of points on the chart indicating the trend direction.
Oscillators
- RSI (Relative Strength Index): Indicates whether an asset is overbought or oversold.
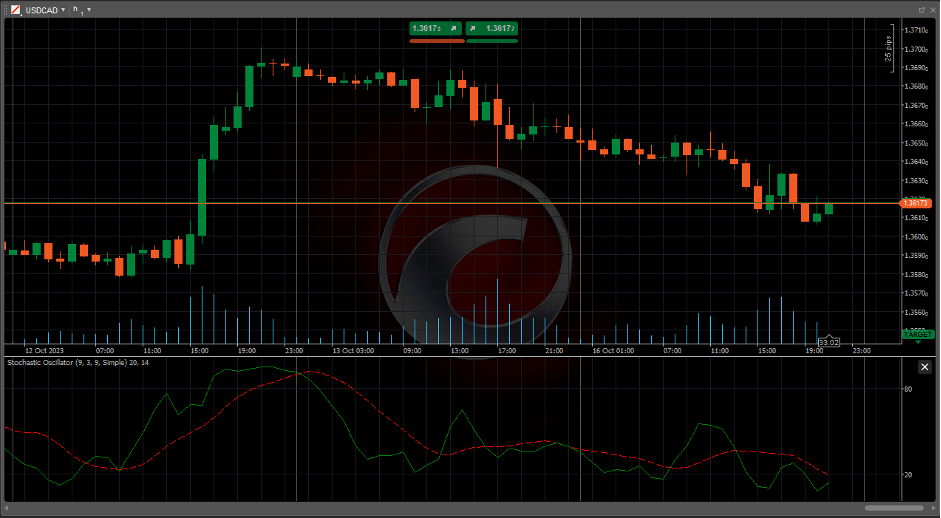
- Stochastic: Also helps determine overbought and oversold levels.
- CCI (Commodity Channel Index): Measures the deviation of an asset’s price from its statistical average price.
Volume Indicators
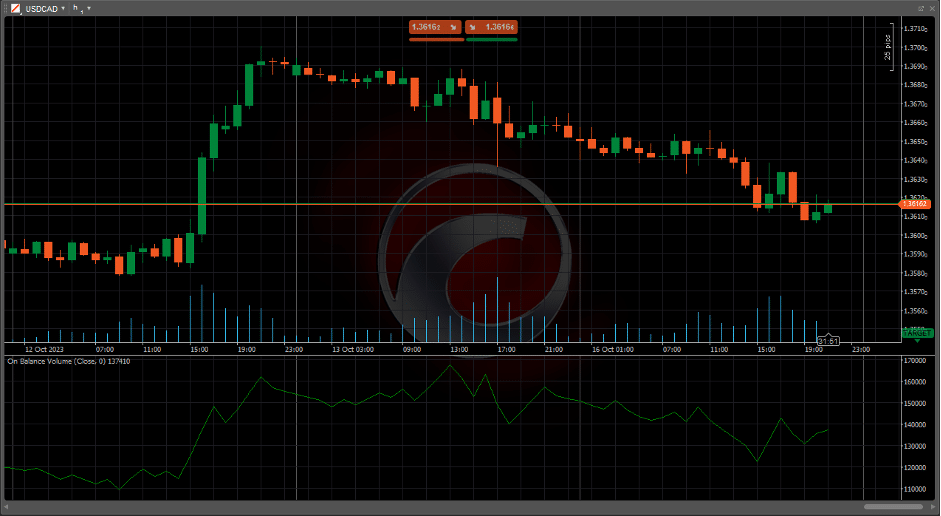
- OBV (On-Balance Volume): Connects volume with price changes.
- Accumulation/Distribution Line: Combines price and volume to show both accumulation and distribution phases.
Reversal and Continuation Patterns
- Head and Shoulders, Double Tops and Double Bottoms, Flags, Pennants, etc.: These are graphical representations of market sentiments and can signal potential trend reversals or continuations.
- Support and Resistance Levels: These levels denote the ranges in which the price of an asset tends to stall or reverse. They are crucial in determining entry and exit points for trades.
- Elliott Wave Theory: This is based on rhythmic patterns and Fibonacci sequences. It provides a comprehensive method of technically analyzing the markets, considering mass psychology, and predicting market movements based on repetitive patterns.
- Dow Theory consists of six fundamental principles describing market behavior. These principles help traders understand and predict future market movements based on past price actions and volumes.
The tools and methods mentioned above can be used individually or in combination to make more accurate forecasts. The choice of a specific method depends on the trader’s preferences, experience, and trading style.
Advantages of Technical Analysis
- Provides a quick way to assess the market.
- Can be applied to both short-term and long-term trading.
- Offers a variety of tools and techniques.
Drawbacks
- Doesn’t consider economic news and events.
- Can be subjective.
Fundamental Analysis Fundamental analysis studies economic indicators and news to predict price movements. This can include news about political events, economic indicators, central bank decisions, and more.
Fundamental analysis examines economic, social, and political factors that could influence the demand and supply in the forex market. Here are some of the most popular trading methods based on fundamental analysis:
- News Trading: Traders monitor significant economic news, such as central bank rate decisions, employment reports, inflation, and other economic indicators. After the data release, traders decide whether to buy or sell a currency.
- Long-Term Trading: Some traders scrutinize a country’s primary economic indicators over an extended period to make decisions about long-term investments.
- Interest Rate Trading: Currencies from countries with higher interest rates often attract more investors, increasing demand for that currency.
- Economic Growth-Based Trading: Countries with rapid economic growth typically lure foreign investors, which can lead to an increased demand for the national currency.
- Geopolitical Event Trading: Political instability or significant international events can cause significant fluctuations in the forex market.
- Balance of Payments Trading: Countries with a positive balance of payments usually strengthen their currency as foreign capital flows into the nation.
- Long-term Trend Trading: By analyzing primary economic indicators and global trends, such as global commodity prices or demographic changes, traders can make decisions about long-term trading.
While technical analysis is often used for short-term decisions, fundamental analysis is typically applied for medium and long-term trading.
Advantages of fundamental analysis:
- Based on actual economic data.
- Suitable for long-term investments.
Disadvantages:
- Requires deep knowledge in economics.
- Can be challenging for beginners.
Manual and Automated Trading: Manual trading is when a trader independently analyzes the market, makes decisions, and executes trades.
Advantages of manual trading:
- Full control over one’s decisions.
- Flexibility in decision-making.
Disadvantages:
- Requires constant market monitoring.
- Emotional decisions can negatively impact results.
Automated trading uses software and algorithms to execute trades based on predefined parameters. Forex robots (Expert Advisors, EAs) are based on various trading strategies. Here are some of the most popular strategies upon which forex robots are built:
1. Trend strategies:
These robots identify the primary market trends and aim to open trades in the direction of this trend. They often use technical indicators, such as moving averages, to determine trends.
2. Scalping strategies:
Scalping robots open many trades on short time intervals, aiming to capture small price movements.
3. Range-based strategies:
These robots trade in sideways market conditions, identifying the upper and lower range boundaries and opening trades on rebounds from these boundaries.
4. News-based strategies:
Robots designed for economic news trading react to significant economic events and data, such as employment reports or interest rate decisions.
5. Breakout strategies:
These robots monitor key support and resistance levels and open trades when the price breaks through these levels.
6. Arbitrage strategies:
Arbitrage robots attempt to profit from this disparity by looking for price differences across different markets or brokerage platforms.
Forex Latency arbitrage (or lag arbitrage) is a trading strategy that exploits temporal differences in asset quotes across different exchanges or brokerage platforms. A latency arbitrage bot is a program or system automatically executing trades based on this strategy.
Here’s how it works:
Data Transmission Delays: Due to various technical and geographical reasons, quotes on one exchange can slightly precede those on another exchange.
Exploiting the Difference: Traders or bots employing latency arbitrage strategy buy an asset where its price is lower and almost instantly sell where it’s higher, profiting from this temporary price difference.
To successfully use this strategy, one requires:
- Fast internet connections: The faster the connection, the quicker the bot can fetch, process data about price differences, and execute corresponding operations.
- High-performance servers: Quick servers allow processing vast amounts of data in real-time.
- Optimized algorithms: To capitalize on price discrepancies as efficiently as possible. However, it’s worth noting that latency arbitrage is a highly competitive strategy, and many exchanges take measures to prevent its use. Additionally, it’s associated with high technical risks and demands substantial initial investments in infrastructure.
7. Grid-based strategies (Grid):
These robots open a series of positions at specific intervals without stop-losses, expecting the market to return to realize a profit eventually.
8. Martingale-based strategies:
These robots double the position size after a losing trade, hoping for the market to rebound and offset losses.
9. Correlation-based strategies:
Robots might trade two or more currencies simultaneously, taking their correlation into account. When selecting or creating a forex robot, it’s vital to understand that there’s no “holy grail” in trading. Each strategy has its advantages and risks. It’s crucial to thoroughly test the robot on historical data and a demo account before deploying it on a real account.
Advantages of automated trading:
- Consistency: Robots execute trades based on predefined algorithms, eliminating emotional decisions.
- Speed: Automated systems can react to market changes faster than humans.
- Availability: Robots can trade 24/7 without taking breaks.
- Multitasking: Can simultaneously monitor multiple markets or currency pairs.
- Backtesting: Ability to test strategies on historical data.
- Disciplined Trading: Avoids the pitfalls of overtrading or missing out on opportunities due to fear or greed.
- Reduced human error: Eliminates mistakes that might occur from manual calculations or order placement.
Trading of Major Players
- Hedge Funds and large asset managers are two key entities in the financial market, and while they have many similarities, they also have a number of differences.
- Hedge Funds:
- Definition: Hedge funds are pools of private capital that are invested to achieve high returns.
- Structure: Typically, hedge funds are less regulated than other investment funds. This allows them to employ more aggressive investment strategies.
- Strategies: Hedge funds can engage in short-term trading, use derivatives, credit arbitrage, currency operations, and much more.
- Investors: Such funds are usually accessible to institutional and large private investors because they have high minimum contributions.
- Payment: Hedge fund managers typically receive a fee as a percentage of assets under management and a share of the profits (usually around 20%).
Large Asset Managers
- Definition: These are companies that manage investments on behalf of others, including individual and institutional investors.
- Types of Assets: Asset managers can manage various assets, including stocks, bonds, real estate, commodities, and more.
- Clients: Their clients may include pension funds, charities, governments, corporations, and individual investors.
- Focus: While hedge funds often focus on achieving maximum returns, asset managers often emphasize long-term stability and aligning the portfolio with the client’s goals.
- Payment: Asset managers typically receive a fee based on a percentage of assets under management.
Similarities and Differences
Both hedge funds and asset managers operate to maximize returns for their clients, but they do so in different ways and with varying degrees of risk. Asset managers typically have a more conservative investment approach than hedge funds. Hedge funds have greater freedom of action due to less regulation, allowing them to employ various strategies to achieve high returns.
Overall, the choice between investing in a hedge fund or working with a significant asset manager depends on the individual or institutional investor’s investment goals, risk appetite, and investment horizon.
