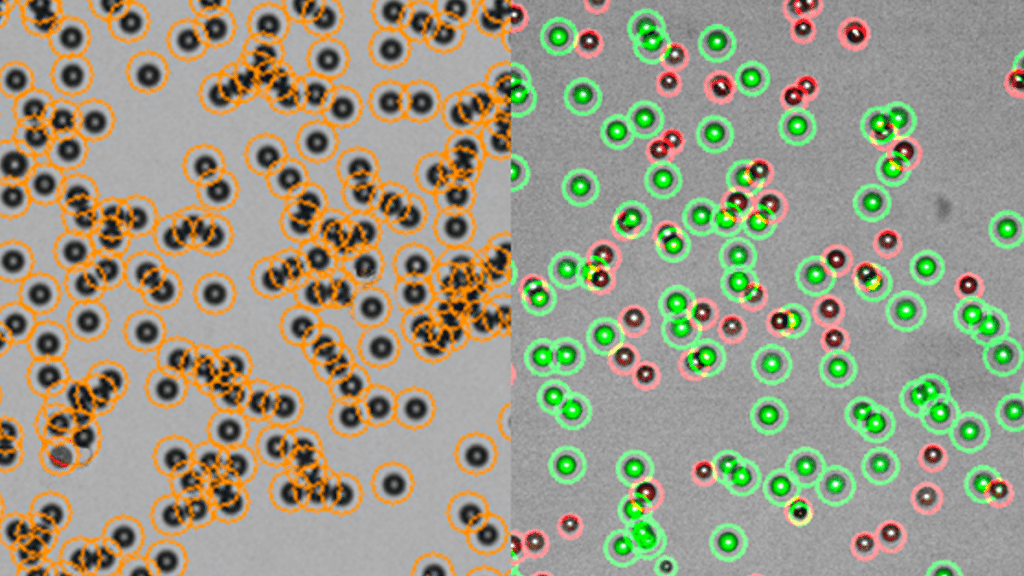
Cell therapy production requires compliance with regulatory standards in order to ensure safety, efficacy, and quality in treatments that have the potential to change lives. Among these regulations, 21 CFR Part 11 particularly focuses on electronic records and signatures. However, this is just one piece of the puzzle. Cell therapy manufacturing intersects with a broad spectrum of regulatory requirements, including Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP), Good Laboratory Practice (GLP), and Good Clinical Practice (GCP). Understanding how 21 CFR Part 11 complements these regulations is crucial for anyone involved in the cell therapy field.
What is 21 CFR Part 11?
21 CFR Part 11 is a regulation issued by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) which sets forth the criteria under which electronic records and electronic signatures are considered trustworthy, reliable, and equivalent to paper records and handwritten signatures.It guarantees that any electronic data managed by pharmaceuticals, biotech, and medical device companies meets strict standards for security, integrity, and traceability.
GMP, GLP, and GCP

Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP), Good Laboratory Practice (GLP), and Good Clinical Practice (GCP) are pillars of the regulatory framework that makes sure medical products are produced consistently and controlled to quality standards. GMP covers the manufacturing and quality assurance of pharmaceutical products, GLP governs pre-clinical laboratory studies, and GCP applies to the clinical trial phase of drug development.
21 CFR Part 11 intersects with these regulations through its emphasis on the integrity and security of electronic records, which are integral to all stages of cell therapy production:
In GMP environments, electronic records such as batch records, quality control data, and equipment logs are essential. 21 CFR Part 11 assures that these documents are accurately and securely retained, allowing for audits and quality checks. For example, an automated cell counter in the manufacturing process may generate data that is crucial for quality control. GMP compliance requires that this data be gathered, kept, and retrievable in accordance with 21 CFR Part 11.
For GLP settings, where pre-clinical studies generate vast amounts of data, 21 CFR Part 11 compliance guarantees that electronic data—from research findings to test results—is reliable and tamper-proof, supporting the validity of the research.
Clinical trial data integrity is extremely important in GCP. 21 CFR Part 11 compliance assures that electronic patient records, trial outcomes, and consent forms meet stringent authenticity and confidentiality requirements, thereby supporting the credibility of clinical research.
Achieving Compliance
Achieving compliance across 21 CFR Part 11 and other regulatory requirements might seem daunting, but it’s a manageable process with a strategic approach. Here are some practical steps:
1. Understand the specifics.
Every regulation has nuances. The first step is to grasp exactly what each demands, particularly how they overlap and complement one another. Tailoring your compliance strategy to these specifics might help to streamline operations and guarantee that no details are ignored.
2. Invest in Compliant Technology
Investing in compliant systems and equipment, such as an automated cell counter that meets 21 CFR Part 11 requirements, can simplify adherence. These technologies not only provide data integrity but also improve efficiency and accuracy in cell therapy production processes.
3. Implement Robust Data Management Practices
Effective data management includes establishing clear protocols for data capture, storage, retrieval, and backup. Ensuring data integrity and security involves both technological solutions and operational practices, such as regular audits and employee training.
4. Build a Culture of Compliance
Compliance should be a shared responsibility across the organization. Regular training and open communication about the importance of regulations like 21 CFR Part 11 and GMP, GLP, and GCP standards can empower employees to maintain compliance in their daily activities.
5. Conduct Regular Audits
Regular internal and external audits help identify potential areas of improvement and ensure that all practices and technologies, including automated systems like cell counters, are up to date with current regulatory standards.
The Role of Regulatory Compliance
It takes a thorough understanding, strategic planning, and dedication to quality and safety to adhere to 21 CFR Part 11 with GLP, GCP, and GMP requirements in the development of cell therapies. By using compliant technologies, implementing robust data management processes, and cultivating a compliance culture, organizations can advance the field of cell therapy, providing hope and healing to patients all around the world. In today’s regulatory world, every detail counts—from the precision of an automated cell counter’s data to the integrity of clinical trial records—all contribute to the greater aim of delivering safe, effective, and innovative therapeutics.
