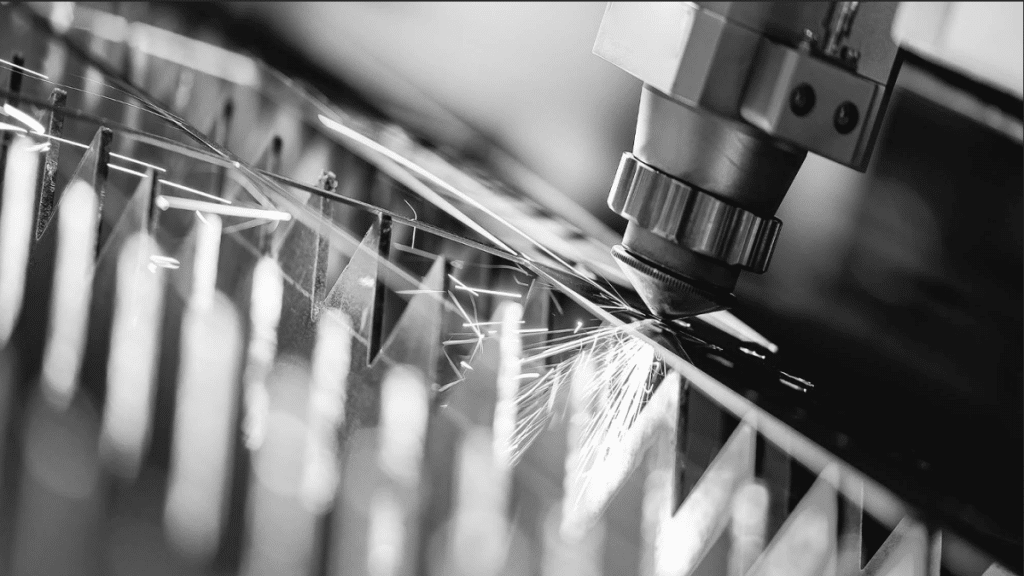
What Does Sheet Metal Fabrication Involve?
Sheet metal fabrication involves transforming flat metal sheets into customized parts with specific shapes and dimensions. This process encompasses several techniques, such as cutting, bending, forming, punching, welding, and finishing. Here’s a step-by-step look at how it works:
Materials Used in Sheet Metal Fabrication
Sheet metal can be made from a variety of materials, each with its own unique properties and applications. Some of the most common materials include:
Stainless Steel: Known for its corrosion resistance and durability, stainless steel is often used in food processing, medical equipment, and marine applications.
Aluminum: Lightweight and corrosion-resistant, aluminum is commonly used in aerospace, automotive, and construction industries.
Steel: Available in hot-rolled and cold-rolled forms, steel is versatile and widely used due to its strength and affordability.
Copper: Excellent electrical conductivity makes copper ideal for electrical components and HVAC systems.
Brass: A combination of copper and zinc, brass is used in musical instruments, plumbing fixtures, and other applications where corrosion resistance is needed.
The thickness of these metal sheets can vary from 0.006 to 0.25 inches, with thinner gauges offering more malleability and thicker ones suitable for heavy-duty applications.
The Sheet Metal Fabrication Process
Design
The process begins with designing the part using Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software. Skilled designers create 3D models and technical drawings that detail material specifications, dimensions, bend angles, and other manufacturing instructions. This step is crucial to ensure the manufacturability and quality of the finished components.
Cutting
Cutting is the initial step in preparing the metal sheet for further processing. This can be done through various methods such as:
Shearing: Using a shear machine to cut the metal sheet.
Punching: Creating holes or shapes using a punch and die.
Laser Cutting: Using high-precision laser cutters to achieve accurate cuts.
Blanking: Cutting out a blank shape from the metal sheet.
These cutting methods utilize CNC (Computer Numerical Control) precision to minimize material waste and ensure accurate cuts.
Bending and Forming
Bending and forming involve reshaping the metal sheet into the desired shape. This can be achieved using:
Press Brakes: Machines that bend the metal at specific angles.
Rolling Machines: Used to bend metal into curved shapes.
Bending Dies: Specialized tools that help in forming custom flanges, lips, and panels.
Bending is a cost-effective method, especially for low to medium-scale production, and is suitable for materials like spring steel, copper, and aluminum.
Punching
Punching is a technique used to create small, precisely positioned holes in the metal sheet. This is often done using CNC punch presses, which can rapidly stamp mounting holes for fasteners, wires, and other features. Punching is an efficient alternative to drilling and ensures high accuracy and reliability.
Welding
Welding is a critical process that joins cut and formed metal pieces into larger assemblies. Common welding techniques include:
- Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW)
- Metal Inert Gas (MIG) Welding
- Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) Welding
- Laser Welding
These techniques involve heating the metal to its melting point and using a filler material to create a strong, metallurgical bond between the pieces.
Machining
Machining operations such as milling, drilling, and grinding are used to create additional features on the metal parts. These processes are essential for creating holes and features for hardware attachment points, airflow, cabling access, or other functional needs. Combining forming capabilities with precision machining maximizes fabrication flexibility.
Finishing and Coating
The final step involves applying various finishing processes to enhance the appearance, durability, and functionality of the fabricated parts. Common finishing methods include:
- Cleaning and Smoothing
- Painting
- Powder Coating
- Hot Dip Galvanizing
- Electroplating
- Anodizing
- Passivation
These surface treatments protect the metal from corrosion, improve its aesthetic qualities, and extend its useful life.
Advantages of Sheet Metal Fabrication
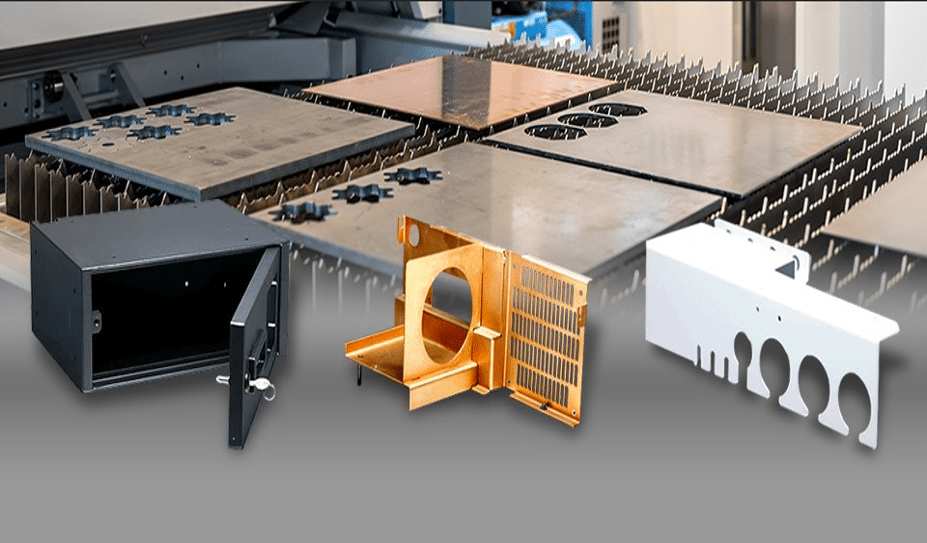
Sheet metal fabrication offers several advantages that make it a preferred method in various industries:
Lightweight Parts Manufacturing
Sheet metal is ideal for producing lightweight components, which is crucial in industries like aerospace and automotive where fuel efficiency is a priority. Lightweight parts help in reducing overall weight, thereby improving fuel economy and efficiency.
Efficiency and Accuracy
The use of advanced machinery and automation in sheet metal fabrication ensures high precision and accuracy. Techniques like laser cutting can achieve cuts with a precision of about 0.0005 inches, minimizing human error and ensuring consistent quality.
Versatility
Sheet metal fabrication can produce a wide range of components, from simple to complex designs. This versatility makes it applicable across various industries, including electronics, construction, and medical devices.
Cost-Effectiveness
Despite the initial investment in machinery, sheet metal fabrication can be cost-effective in the long run. It allows for rapid prototyping and production, reducing the time and cost associated with traditional manufacturing methods.
Applications of Sheet Metal Fabrication
Sheet metal fabrication is ubiquitous and finds applications in numerous industries:
Aerospace: Components such as aircraft wings, engine parts, and other structural elements.
Automotive: Vehicle panels, engine components, and other automotive parts.
Construction: HVAC ductwork, roofing materials, and structural elements.
Electronics: Enclosures, casings, and other electronic components.
Medical: Equipment, devices, and other medical tools.
Food Processing: Equipment and machinery used in food processing industries.
Conclusion
Sheet metal fabrication is a dynamic and essential discipline in the manufacturing world. It combines advanced techniques, machinery, and materials to produce customized parts with high precision and accuracy. Understanding the processes, materials, and advantages of sheet metal fabrication can help in leveraging this technology for a wide range of applications. Whether it is for producing lightweight aircraft components or durable construction materials, sheet metal fabrication stands out as a versatile and efficient manufacturing method.