Plastic sheeting has become a go-to material for countless industries due to its versatility, cost-effectiveness, and durability. With so many types available – each offering unique properties and benefits – understanding the differences between them is crucial for making the right choice. Whether you’re looking for flexibility, impact resistance, or weatherproofing, plastic sheeting has a solution for almost every need. Read on to explore the various types, their characteristics, and how they’re used in different industries.
Types of Plastic Sheeting

Whether you’re in construction, crafting, or any other industry that requires reliable materials, durable and versatile plastic sheets can meet your needs. With various thicknesses, colours, and finishes available, they allow for creative and practical solutions in almost any setting. So, what are the most common thermoplastics? Here’s an overview of the most popular options, each with its unique properties:
- ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): ABS is among the most widely used thermoplastics, especially in thermoforming. Its broad forming temperature range allows for easy shaping, and it boasts good dimensional stability, which simplifies trimming. Its specific gravity is around 1.08, making it a lightweight yet robust choice;
- Acrylic: Acrylic is highly versatile and easy to work with. Tanning bed acrylic replacement sheets are highly popular due to several beneficial properties. Their clarity allows maximum UV light penetration, essential for effective tanning. Additionally, acrylic sheets are lightweight, durable, and resistant to shattering, making them safer than glass;
- HIPS (High Impact Polystyrene): HIPS is known for being cost-effective and easy to thermoform. It’s a great option for point-of-sale displays and has a specific gravity of 1.05. This material is moisture-resistant, which means pre-drying isn’t usually necessary;
- SAN (Styrene Acrylonitrile): Similar to HIPS, SAN provides better chemical resistance and can be UV stabilised. It has a blueish tint in its clear grades and a specific gravity of about 1.08;
- Polypropylene (PP): Polypropylene plastic sheets offer good fatigue and chemical resistance, but they can be challenging to form due to their narrow temperature range. This material’s specific gravity is lower, at around 0.92, making it a lightweight option;
- HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene): Known for its low-temperature impact resistance and good welding properties, HDPE is slightly denser than PP with a specific gravity of about 0.95. However, it doesn’t handle UV exposure well unless coloured;
- PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol Modified): PETG has excellent forming properties and impact strength, though it’s typically not UV resistant. It has a specific gravity similar to acrylic at 1.2;
- Polycarbonate: Known for their impressive impact strength and stiffness, polycarbonate plastic sheets for sale require pre-drying due to moisture absorption. This material’s specific gravity is also around 1.2, and some grades come UV-resistant;
- Construction PVC is easy to fabricate and has good impact resistance, although it becomes brittle in low temperatures. Its specific gravity is about 1.4, making it one of the denser options;
Plastic Sheet Applications
Construction

Plastic sheeting has become a staple in the construction industry thanks to its versatility and affordability. It serves a variety of purposes, primarily as a protective wrap for building materials, insulation, and other components during construction. But it doesn’t just stop there; it can also be creatively used as wallpaper, adding a unique visual element to interior spaces.
Another essential application of plastic sheeting in construction is as a vapor barrier. Plastic wall sheets are placed strategically between the interior and exterior of a building to prevent moisture infiltration. This is crucial in humid regions or areas at risk of flooding. By creating a moisture barrier, plastic sheeting not only protects the structure but also contributes to energy efficiency by improving insulation.
Plastic wall sheets are often used in basements and crawl spaces to combat moisture and prevent potential structural harm. Moreover, these materials provide protective wraps around insulation and other materials, safeguarding them against environmental factors like dust and weather. Using thermoplastics in construction allows for innovative design options and can lead to cost savings in certain situations. However, the choice of material will depend on the specific requirements of your project, including structural needs, environmental factors, and aesthetic goals.
Signage

Acrylic, impact-modified acrylic, and polycarbonate have been the go-to materials for indoor and outdoor signage for the past three decades, and it’s easy to see why. These materials are lightweight and easy to work with, making them ideal for various applications.
Acrylic, often known as plexiglass, is produced with UV inhibitors, which help it resist damage from sunlight, ensuring it lasts for years. This is why it’s commonly used for tanning bed acrylic replacement sheets, ensuring they remain clear and effective over time. Because of its inherent strength, this material is also favoured for applications that require precise shaping, such as in channel letter production.
Impact-modified acrylic shares many characteristics with standard acrylic, including UV stability. However, it takes things a step further by incorporating varying levels of rubberization for enhanced durability. The most common grades, are about 50% to 70% impact-modified, making them significantly tougher.
Polycarbonate sheets, are often considered the champions of strength and durability. They are incredibly tough, boasting a strength that is 200 times greater than glass and 15 times more robust than standard acrylic sheets. This makes polycarbonate the ideal choice for signage in areas prone to extreme wear and tear.
These materials shine when paired with LED lighting, as they provide excellent light transmittance, enhancing visibility and aesthetics. To minimise hotspots from direct lighting, you can use diffuser film for standard panels to achieve a more uniform glow. You’ll find these materials commonly used in various signage applications, including channel letters, monument signs, cabinet signs, pylon signs, and even interior displays.
Car Interiors
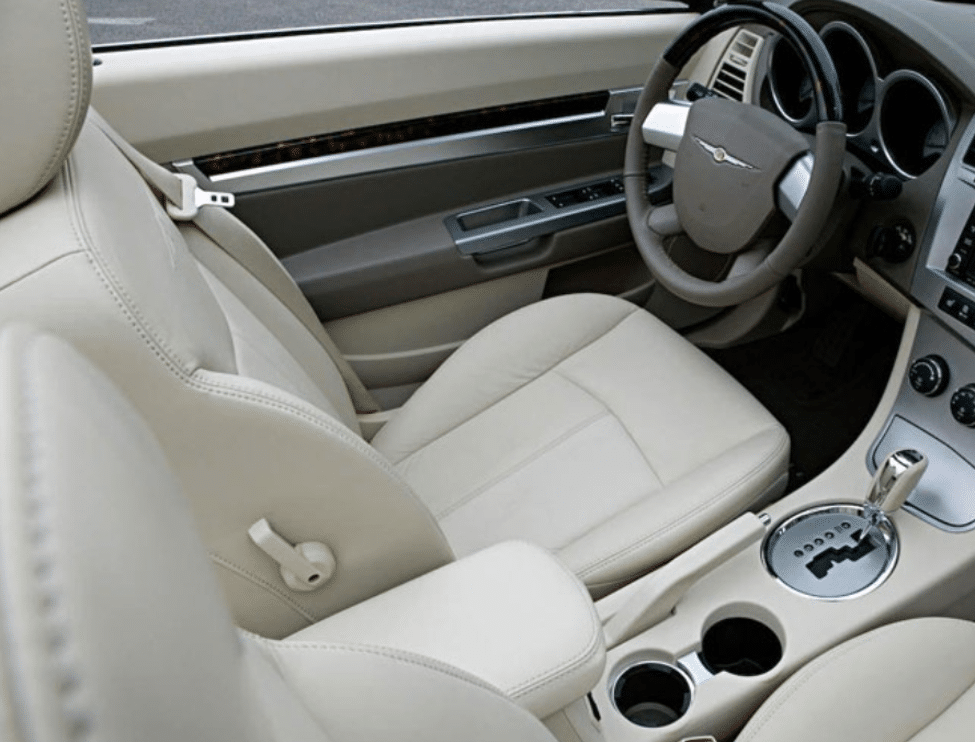

When you enter a car, the plastics around you play a vital role in comfort and safety. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is commonly used for parts like instrument panels due to its adaptability and flame-retardant properties. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is found in dashboards, known for its strength and impact resistance. Polystyrene (PS) enhances visual appeal in buttons and displays, while polyethylene (PE) adds comfort to seat cushions and carpeting.
Polycarbonate (PC) is a durable choice for window controls and safety equipment, ensuring longevity. Lastly, polyurethane (PU) mimics leather in upholstery, providing a luxurious feel without the high cost. Together, these materials create a functional and inviting driving experience.