Designing and producing power-intensive printed circuit boards (PCBs) poses special challenges in the quickly changing electronics sector of today, necessitating advanced thermal management techniques. To ensure optimal performance and dependability, sophisticated thermal modeling techniques have become increasingly important as electronic devices get more powerful and smaller. Advanced techniques used in thermal modeling for high-power PCB designs are thoroughly examined in this post.
Comprehending Thermal Issues in Contemporary PCB Architecture
With the growing demands for downsizing and increased computing capacity, the field of design PCB has seen a significant transformation. During operation, power-intensive components produce a lot of heat, so thermal management is an essential part of PCB design. In order to preserve the delicate balance between performance, reliability, and cost-effectiveness, engineers and designers must carefully take heat restrictions into account. For designs coming from sophisticated semiconductor manufacturing regions, such as the USA, where PCB design innovation is still pushing boundaries, this is especially pertinent.
Thermal Simulation’s Development in PCB Design
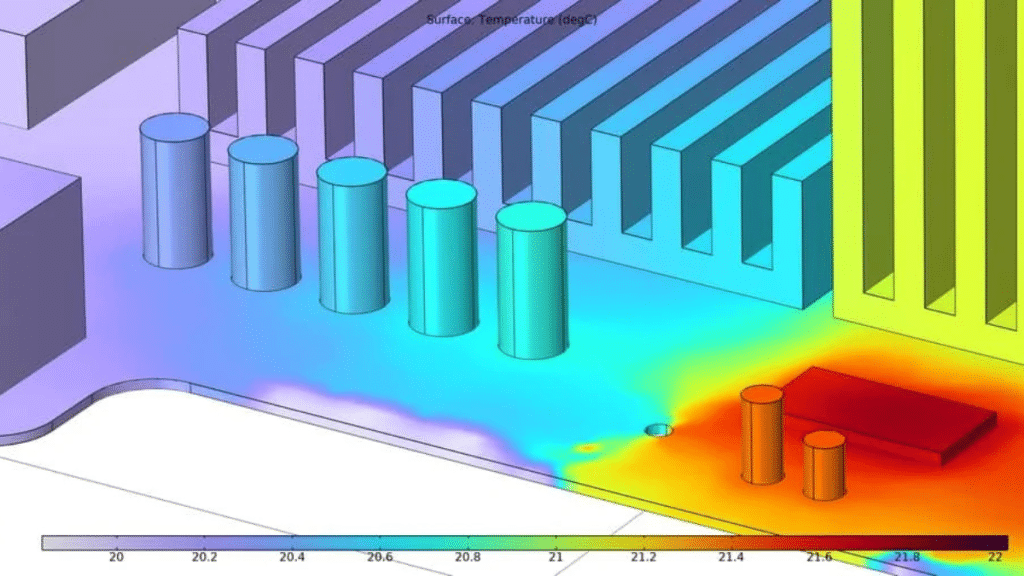
Simplified computations and empirical testing were frequently used in traditional thermal management techniques, which were unsuitable for the intricate designs of today. Sophisticated multi-physics simulations and computational fluid dynamics (CFD) models are now part of contemporary thermal simulation methods. The need for expensive physical prototypes and design iterations is greatly reduced because of these sophisticated technologies, which allow designers to forecast thermal behavior with previously unheard-of accuracy.
Important Elements of Complex Thermal Simulation
Several physical phenomena are integrated into contemporary thermal simulation platforms to offer thorough investigation. Conduction, convection, and radiation are examples of heat transfer mechanisms that are modeled concurrently with electrical performance attributes. This all-encompassing strategy guarantees that electrical functionality won’t be harmed by thermal solutions, and vice versa. The simulation software optimizes thermal performance by taking into account elements including cooling solutions, copper distribution, layer stack-up, and component positioning.
Putting Advanced Cooling Techniques into Practice
Before deployment, designers can assess several cooling solutions using thermal modeling. Analyzing the performance of sophisticated materials, cooling fans, heat sinks, and thermal vias is part of this. The placement and dimensions of these cooling components are optimized with the aid of the modeling tools, guaranteeing optimal heat dissipation while adhering to design limitations. This feature is especially helpful when dealing with high-performance semiconductor parts that need to be precisely managed in terms of temperature.
Thermal Considerations and Material Selection
Designers can assess the effects of various PCB materials on thermal performance thanks to sophisticated thermal simulation. To ascertain their efficacy in certain applications, high-thermal-conductivity materials, specialist thermal interface materials, and sophisticated substrate technologies might be modeled. For designs that demand the best thermal performance, particularly in power-intensive applications, this capability is essential.
Thermal Analysis and Optimization in Real Time
Real-time analysis capabilities provided by contemporary simulation systems enable designers to make quick modifications in response to thermal performance data. This iterative process aids in the early detection of thermal bottlenecks and possible hotspots during the design phase. Engineers can rapidly assess various component locations and routing techniques to maximize overall heat distribution.
Connectivity with Production Procedures
The impact of manufacturing processes on thermal performance is now taken into account using thermal simulation tools. This entails examining the impacts of various surface treatments, plating thicknesses, and copper weights. With such thorough study, the finished PCB is guaranteed to meet thermal requirements while still being able to be built within predetermined tolerances.
Sophisticated Validation and Verification Techniques
Modern thermal simulation systems use sophisticated verification techniques to guarantee precision. Correlation with physical measures, thermal imaging data, and past performance data are examples of this. By using these validation methods, simulation models can be improved and future designs’ forecast accuracy raised.
Influence on Time-to-Market and Design Process
Using sophisticated thermal modeling methods has had a big impact on the PCB design in usa process. Potential problems can be found and fixed using early thermal analysis before moving further with actual prototypes. Reliable thermal performance is ensured while development cycles are shortened and time-to-market is accelerated with this proactive strategy.
Prospects for Thermal Simulation
As PCB designs continue to change, new issues are being met by the advancement of thermal simulation tools. In order to increase forecast accuracy and optimization capabilities, simulation programs are incorporating artificial intelligence and machine learning techniques. These advancements are especially pertinent to intricate designs with high-power applications and sophisticated semiconductor components.
Recommended Procedures for Using Thermal Simulation
A systematic methodology is necessary for thermal simulation to be implemented successfully. Clear thermal criteria must be established, component models must be made in detail, and simulation results must be verified against actual data. Maintaining accuracy as designs and technologies change requires regular calibration of simulation models.
Evaluation of Advanced Thermal Simulation’s Cost-Benefit
Even while using sophisticated thermal modeling tools necessitates an initial outlay of funds, the long-term advantages frequently outweigh the expense. Significant cost savings throughout the product life cycle are a result of fewer prototype iterations, higher first-pass success rates, and improved product reliability. This is especially important for intricate
designs that need accurate thermal control and sophisticated semiconductor components.
A best semiconductor company proves its excellence through extensive research and development abilities and innovative manufacturing practices and robust quality control systems and secure intellectual property resources. Leading companies in the industry maintain current fabrication facilities and invest strongly in innovation for delivering reliable products through their ability to adapt to market changes.
Conclusion:
In today’s PCB design, advanced thermal simulation techniques are essential tools, especially for applications requiring a lot of power. As performance needs become more rigorous, the ability to precisely forecast and optimize thermal performance early in the design phase helps guarantee dependable operation. Thermal simulation will only become more significant in PCB design as technology develops, spurring additional advancements in this crucial area.
The incorporation of these cutting-edge thermal modeling methods has completely changed PCB design procedures, especially in areas like the USA that are renowned for their innovative semiconductors. These technologies enable designers to make more dependable and effective PCBs while cutting down on development time and expenses by enabling more precise prediction and optimization of thermal behavior. Sophisticated thermal simulation in PCB design will become even more crucial as the electronics industry develops, making it a necessary skill to remain competitive in this fast-paced sector.