Thermal management plays a critical role in every Energy Storage System (ESS). Proper temperature control ensures battery safety, enhances energy conversion efficiency, and extends system lifespan.
Among various cooling methods, air and liquid cooling are the two most widely used in ESS designs today. Air cooling relies on forced ventilation to remove heat, while liquid cooling uses a circulating coolant to regulate temperature more precisely.
The purpose of this article is to provide a clear comparison of these two technologies so that you can choose the right system for your needs.
Picture shown: Air cooling energy storage system
Air or Liquid Cooling: Regular Air Cooling Energy Storage Systems Explained
Air-cooled energy storage systems are the most common thermal management solution, particularly for small- to mid-scale applications. They use fans or blowers to circulate ambient air through the battery cabinet, dissipating heat from cells and electronic components.
This system brings the following advantages:
Advantages of Air Cooling Energy Storage Systems
- Cost-Effective Design: Air cooling systems are simpler and cheaper to manufacture and maintain, making them perfect for cost-sensitive projects.
- Easy Installation and Maintenance: With no liquid handling or complex piping, installation is straightforward, and routine maintenance is minimal.
- Suitable for Moderate Climates: Performs well in environments where ambient temperatures are stable and not excessively high.
Limitations of Air Cooling Energy Storage Systems
- Lower Cooling Efficiency: Air typically has a lower heat capacity than liquids, resulting in less effective temperature regulation under heavy loads.
- Uneven Temperature Distribution: Larger battery packs can experience hot spots, which affect performance and accelerate battery aging.
- Limited for High-Density Applications: As ESS capacities increase, air cooling becomes less efficient and noisier due to high airflow requirements.
Typical Applications
Air-cooled ESS are commonly used in residential and small commercial installations, telecom base stations, and areas with moderate climates. They are also suitable for mobile or modular systems where compactness and simplicity matter more than extreme cooling performance.
Air or Liquid Cooling: Liquid Cooling Energy Storage Systems Explained
Liquid-cooled energy storage systems use a closed-loop liquid circuit, typically with water, glycol, or specialized coolant, to absorb and transfer heat away from battery cells. The coolant flows through pipelines integrated into the battery modules and is then cooled through a heat exchanger or radiator.
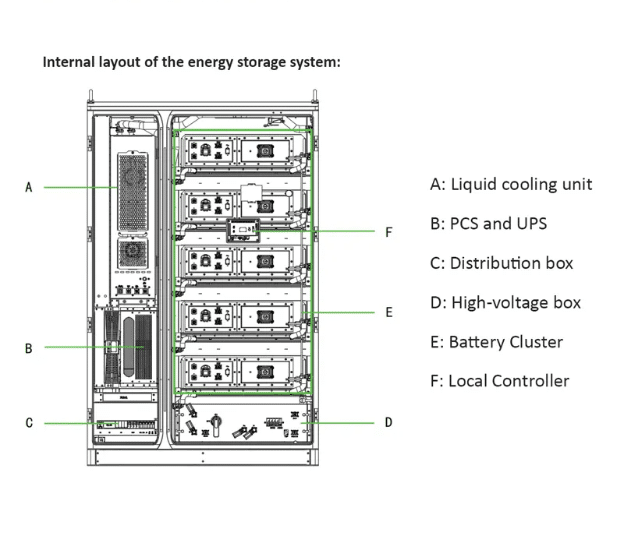
Picture shown: Liquid cooling energy storage system
Here is a quick look at the pros and cons of the liquid cooling systems in this air vs. liquid cooling system comparison guide:
Advantages of Liquid Cooling Energy Storage Systems
- Superior Thermal Uniformity: Delivers consistent temperature control across all battery cells, minimizing hot spots.
- High Efficiency Under Heavy Loads: Maintains stable temperatures even when systems operate at high power density or during rapid charge-discharge cycles.
- Longer Battery Lifespan: Reduces thermal stress and degradation, extending the operational life of the batteries.
- Compact Design: Allows for tighter battery arrangements, increasing energy density without overheating risk.
- Adaptability to Harsh Environments: Performs reliably in high-temperature or industrial settings where air cooling struggles.
Limitations of Liquid Cooling Energy Storage Systems
- Higher Initial Cost: Requires pumps, heat exchangers, and coolant management components, which raises upfront investment.
- Complex Maintenance: Periodic coolant checks and leak prevention systems are needed to maintain efficiency.
- More Installation Requirements: Proper design and sealing are essential to prevent leakage and ensure long-term reliability.
Ideal Applications
Liquid cooling is preferred for large-scale energy storage installations such as grid-connected power stations, industrial facilities, and electric vehicle charging stations. It is also well-suited for high-capacity applications that demand continuous operation and precise thermal control.
Table Comparison of Air vs. Liquid Cooling Energy Storage Systems
Here is a table summarizing the information about air vs. liquid cooling systems:
| Feature | Air Cooling ESS | Liquid Cooling ESS |
|---|---|---|
| Cooling Medium | Ambient air | Liquid coolant (water, glycol, etc.) |
| Efficiency | Moderate, suitable for smaller systems | High, stable under heavy loads |
| Temperature Uniformity | Good, yet prone to hot spots | Uniform and consistent |
| Maintenance | Simple, low cost | Requires regular coolant checks |
| Installation Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Noise Level | Higher due to fans | Lower operation noise |
| Energy Density Compatibility | Limited for high-density setups | Ideal for high-density systems |
| Best Application | Residential, telecom, small commercial | Industrial, grid-scale, EV charging |
Pro Energy Storage System Manufacturer Recommendation
A trusted manufacturer is essential when investing in air and liquid cooling systems, and Sunway stands out for its engineering excellence and consistently reliable product performance.
With strong expertise in photovoltaic and energy storage technology, the company provides a wide range of commercial and industrial ESS solutions (C&I ESS) tailored to different power needs and environmental conditions.
Its product lineup includes both air-cooled and liquid-cooled systems, such as the Sunway Intelligent Air Cooling 50 kW 100 kWh and the Sunway Liquid-Cooled 100 kW 261 kWh Outdoor Cabinet Energy Storage System, each designed for stable operation, efficient heat management, and long service life.
Every system integrates high-quality batteries, smart inverters, and intelligent cooling control to ensure safety, durability, and consistent performance. Built in advanced manufacturing facilities, Sunway’s ESS products meet strict quality standards and are widely used in commercial buildings, factories, and renewable energy projects.
Wrapping Up
Choosing the right air or liquid cooling energy storage system depends on the application, scale, and environmental conditions. Air-cooled systems offer cost-effective, simple, and easy-to-maintain solutions for small- to mid-scale projects with moderate temperatures.
In contrast, liquid-cooled systems provide superior thermal uniformity, higher efficiency under heavy loads, and longer battery lifespan. This makes them ideal for large-scale, high-density, or industrial applications.
Partnering with a reliable manufacturer like Sunway ensures both air and liquid cooling systems deliver safe, durable, and high-performance energy storage solutions. For advice suited to your situation, just click here to get in touch.