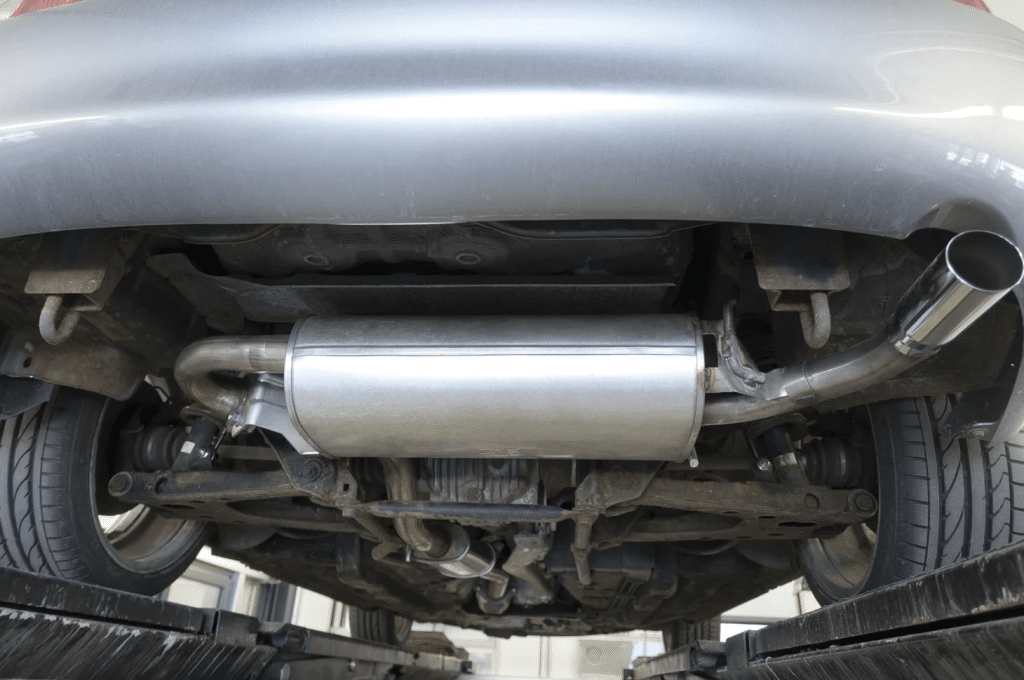
The catalytic converter on a Toyota Tundra plays a crucial role in reducing the vehicle’s emissions. It is a component of the exhaust system that converts harmful pollutants in the exhaust gas into less harmful substances before they are released into the environment. Given the importance of this device for both environmental protection and the vehicle’s performance, understanding its function and maintenance is vital for Tundra owners.
As environmental regulations become stricter, the efficiency and condition of catalytic converters have gained attention. Vehicles like the Toyota Tundra are equipped with advanced catalytic converters designed to meet these stringent standards and ensure a lower impact on the environment. Regular inspection and timely replacement of the catalytic converter are essential, as a failing unit can lead to reduced fuel efficiency, increased emissions, and potential damage to the vehicle’s engine.
Theft of catalytic converters has become increasingly common due to the precious metals they contain, such as platinum, palladium, and rhodium. As a result, Tundra owners must also consider protective measures to secure their vehicle’s catalytic converter. From installing anti-theft devices to parking in secure areas, there are several strategies to deter potential theft and safeguard this critical component.
Overview of Tundra Catalytic Converters
Catalytic converters are critical components in the exhaust systems of modern vehicles, including the Toyota Tundra. Their primary function is to reduce harmful emissions from the engine by converting toxic gases into less harmful substances before they are released into the atmosphere.
The Toyota Tundra catalytic converter typically features a honeycomb structure lined with precious metals like platinum, palladium, and rhodium. These metals act as catalysts, promoting chemical reactions that transform carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and unburned hydrocarbons into carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and water vapor.
Installation and Compatibility:
- The Tundra catalytic converter is designed to integrate seamlessly with specific model years and engine types.
- It is typically located beneath the vehicle, between the exhaust manifold and the muffler.
Maintenance and Issues:
- Regular maintenance ensures optimal performance and longevity. It includes inspecting for clogs or damage during routine service checks.
- Common issues include reduced engine performance and increased emissions due to clogging or internal damage.
Legislation and Compliance:
- Vehicles are required to meet specific emission standards set by legislation such as the Clean Air Act.
- Toyota Tundra owners must ensure their catalytic converters comply with these regulations to pass emission tests and maintain legality on the road.
Replacement and Cost:
- If a catalytic converter fails, it must be replaced to restore proper function and compliance with emission laws.
- Replacement costs vary, but they can be significant due to the precious metals used in the converters.
Components and Materials
In a Tundra catalytic converter, the efficiency and longevity are predicated on the quality of the components and materials used in its construction.
Catalyst Materials
The core catalyst materials in a catalytic converter are typically platinum (Pt), palladium (Pd), and rhodium (Rh). These precious metals facilitate the chemical reactions that convert harmful exhaust gases into less toxic substances. Specifically, platinum and palladium are used for the oxidation of hydrocarbons and carbon monoxide into carbon dioxide and water, while rhodium is used to reduce nitrogen oxides to nitrogen and oxygen.
- Platinum: Used for its stability and oxidation capabilities.
- Palladium: Serves a similar purpose to platinum but is often used due to its lower cost.
- Rhodium: A rare material used for its reduction properties.
Converter Housing
The housing of a catalytic converter is constructed from stainless steel to resist high temperatures and corrosion. The housing must maintain its integrity over a wide range of operating temperatures and conditions to protect the internal components from external damage.
- Material: Stainless steel
- Properties: High-temperature resistance, corrosion resistance
The internal structure of the housing includes a ceramic or metallic honeycomb substrate that supports the catalyst materials. This substrate needs to have a high surface area to maximize contact with exhaust gases.
- Substrate Types: Ceramic or metallic
- Function: Supports catalyst materials, maximizes surface area
Function and Efficiency
In the context of the Tundra’s catalytic converter, its primary roles are minimizing harmful emissions and maintaining a balance with performance, all while adhering to strict regulatory standards.
Emission Reduction
The catalytic converter on a Tundra is designed to reduce the emissions of nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide, and hydrocarbons. It achieves this by promoting a chemical reaction that converts these gases into less harmful substances like nitrogen gas, carbon dioxide, and water vapor.
Impact on Performance
While the Tundra’s catalytic converter is crucial for emission control, it is engineered to have a minimal impact on the vehicle’s performance. The exhaust flow is optimized to ensure that the reduction of pollutants does not significantly affect engine power or fuel efficiency.
Regulatory Compliance
Catalytic converters are a key component for vehicles like the Tundra to meet emission regulations. They are designed to keep the vehicle compliant with environmental standards such as those set by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and California Air Resources Board (CARB).
Common Issues and Maintenance
Catalytic converters in Tundras are crucial for reducing emissions, yet they face risks of theft and can suffer from performance issues. Proper maintenance is essential to mitigate these problems.
Catalytic Converter Theft
The theft of catalytic converters from vehicles, including the Toyota Tundra, has become a significant issue due to the value of the precious metals they contain. Owners can take preventative measures by:
- Parking in Well-Lit Areas: Discourages potential theft
- Installing Security Devices: Such as alarms or catalytic converter guards
Signs of Failure
A failing catalytic converter can exhibit several signs, including:
- Reduced Performance: Struggling acceleration and decreased power
- Check Engine Light: Often triggered by failure codes from sensors
- Rattling Noises: May indicate internal damage
Maintenance Tips
Regular maintenance helps ensure the longevity of a Tundra’s catalytic converter. Owners should:
- Use the correct fuel grade: Avoid lower octane fuels that can lead to build-up
- Keep up with engine maintenance: Poor engine performance can damage the converter
- Regular inspections: Early detection and repair of exhaust system issues
Regular checks by Ohio Toyota dealers and adhering to the vehicle’s maintenance schedule play a critical role in preventing catalytic converter issues.
Installation and Replacement
Replacing or installing a catalytic converter on a Tundra involves several steps which should be followed meticulously to ensure proper function and compliance with emission regulations.
Preparation:
- Ensure the vehicle is on a flat surface and the engine is cool.
- Gather all necessary tools, including a socket set, wrenches, and a jack with stands.
Removal:
- Lift the Tundra using a jack and securely place it on stands.
- Locate the catalytic converter on the exhaust system.
- Spray penetrating oil on bolts and fasteners and allow it to sit to loosen them.
- Use appropriate sockets to remove bolts or nuts securing the catalytic converter.
Installation:
- Carefully align the new catalytic converter with the exhaust system.
- Attach the new converter using new hardware if supplied, otherwise, inspect and reuse the old hardware if it’s in good condition.
- Securely tighten all fasteners to the manufacturer’s specified torque.
Post-Installation Checks:
- Lower the vehicle from the stands.
- Start the engine and listen for any unusual noises which may indicate a leak.
- Confirm that there are no Check Engine lights or error codes, indicating a successful installation.
Note: It’s recommended to consult the vehicle’s service manual for specific instructions and torque values. Additionally, in some jurisdictions, catalytic converter replacement must be performed by a certified professional and may involve re-programming the vehicle’s computer system. Always ensure that the replacement part complies with local emission standards.