Lamination Manufacturing accelerates manufacturing drastically, slicing the lead times to a fraction of the times of outdated techniques. Modern technologies that are user-intuitive augment the process by providing high accuracy and productivity, minimizing error and reworking. In many cases, we are able to improve the material and produce techniques that are exclusive to our company making not only designs that last but also perform at the highest level.
Digital modeling is the key to optimizing designs for press-on repeat and continuous improvement, which culminate in the best results. Aided by efficient workflows and agile techniques, fast mold manufacturing adorns tech innovators with the reputation of being knowledgeable of what the global market requires.
Understanding Mold Design and Material Selection!
Design Basics
The design is a key factor when employing FMM (fast mold manufacturing). Begin with CAD geometry models to determine the shape of the part, obtaining a mold flow analysis done right.
DFM is a concept that helps to avoid unreasonable complexity which contravenes the main rule expected to reduce the cycle time. The basic parts are to be done such as heat blocking, ejector pins, and parting lines. Make use of modular molds, which allow for flexible choices.
Material Criteria
Stuffing material is a necessary part of FMM’s effectiveness. High-standard materials such as the C20 or H13 type of steel would enhance the durability of the tool and assist in rapid heat dissipation.
The viscosity of the resin is definitely a factor to consider; consider low-temperature grades of resins to decrease injection pressures. Mixing mold material with plastic softens product hardness adequately, which makes it withstand for a longer working period.
The Role of CAD/CAM in Modern Mold Making!
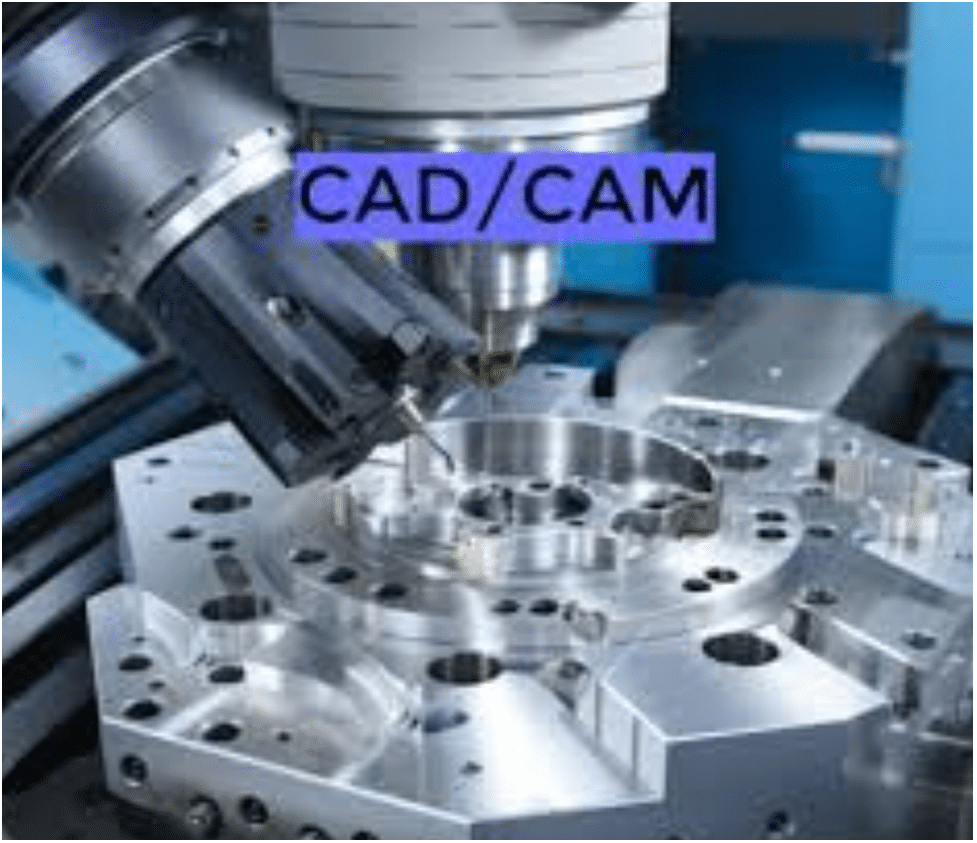

CAD/CAM Integration
In the FMM environment, CAD/CAM integration is the key element. Using CAD, it is possible to prepare a 3D mold design, which is then CAM’s source for translating these designs into machine-readable instructions. This harmony is a vehicle for accelerating contour production, reducing manual mistakes, and guaranteeing their dimensional integrity by turning up to the required specification. Integration ensures design-to-product workflow operations.
Efficiency Impact
The FMM needs CAD/CAM to develop its competitive strength in the production domain. Besides, the automated machining procedure reduces the production time considerably.
The speed of the prototype makes it achievable even if the chances for adjustment and validation are higher. The physical manipulation is eliminated, thus the time saved, and the involved parties here are reduced. Essentially, CAD/CAM has been transforming the manufacturing timelines; therefore productivity has been speeding up.
Precision Influence
CAD/CAM technologies make for the most precise kind of FMM processing. CNC machinery is automating the mold creation process, resulting in very tight tolerances and fine details.
Complex algorithms help in precision construction that is achieved with accuracy, thus, a lot of scrap material is curbed. Feeds back errorless fitting of components speed up amendment time and, consequently, increases in part functionality. It is also worth mentioning that the improved product quality is a consequence.
Step-by-Step Guide to Mold-Making Process!
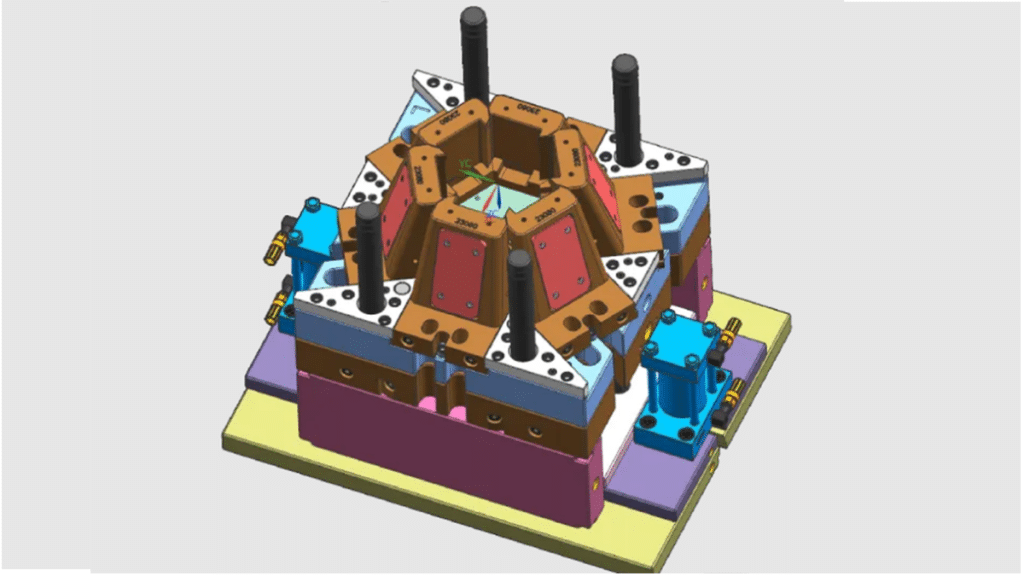
Mold Designing
To start with, develop a solid CAD model concentrating on the *part* geometries of the product. Including early designing of crucial elements, cooling and cooling systems follow the Design for manufacturing recommendations when thinking of mold, aiming to get an easier mold without undercuts. Key parts: apertures, bolts, and ejectors. Molds should be created in such a way that they join together perfectly leading to no flash and shorter cycle times.
Thermoplastic Selection
We need to perfect our product because it is FMs masterpiece; it has to be made with the right thermoplastic material. It is better to use lower viscosity materials which cool on a fast pace. Consider ABS or PP for their blend of special-flow and high-strength properties.
Consider thermal and chemical performance of the adhesive and match it with the usage purpose. Material selection plays a role in the mold design, the amount of time required for molding and the final part quality.
Machine Setup
FMM establishment without losses depends on efficient plant setup. Attaining CNC machines to be of the same caliber as the CAD/CAM outputs aligned has to do with precise tool paths.
Setup comes with configure the injection molding machine with amendment on the temperature and pressure setting according to the selected thermoplastic. Correct positioning of all molds results in less wastages and improved product quality.
Adjustments
The rapidity is put into practice along the whole journey, which is one of the most important factors that make the movie enjoyable. Be sure to closely inspect first runs to watch out for defects such as sinking or warping. There must be machines settings change, including injection rate or cooling time, guided by the data collected in real-time. Changing molds or processes rapidly will undoubtedly lead to production interruption and material loss while wastage is reduced.
Key Techniques in Fast Mold Fabrication!
Fabrication Processes
Proofing for fast mold manufacturing begins with mapping notch in the process of production. Some of the principal competitors of injection molding, CNC machining, and 3D printing are highlighted. Its complexity level and production cycle period are dependent on production volume as well as mold complexity.
In the case of large quantities, injection molding distinguishes itself, CNC machining ensures paranoia of the most complex molds, and 3D printing wins the competition by the speed of rapid prototyping development.
Precision Machining
To be a better in the area of short-term mold production, the detail placing is the vital thing. Manufacturers are able to make close tolerance products and fine detailing through the use of modern technology, i.e., high-speed CNC machines. There is aiming at minimizing repeating processes and at the same time ensuring the mold’s surface finish meets the requirements.
The manufacturer may have a tooling set consisting of classic tools like end mills, drills, and lathes that are responsible for much of this work. CAM advancements in software also help in getting this done by optimizing the machining paths for applicable speed and efficiency.
Tooling Importance
Machinery and tooling are the main characteristics that are used in manufacturing the molds in a short span. The right tools will decrease the mold-making time and have the potential to improve the results. Robustness and precision in temperature of steel or aluminum casting are desirable for their use in buildings.
Two of the technologies employed in these processes are ED (Electric Discharge Machining) and HSM (High-Speed Machining), which are used to decorate the mold details. Continuous inspection, and calibration of tools, help achieve level production and lessen the time of mold replacement.
Injection Molding Process From Melting to Molding!
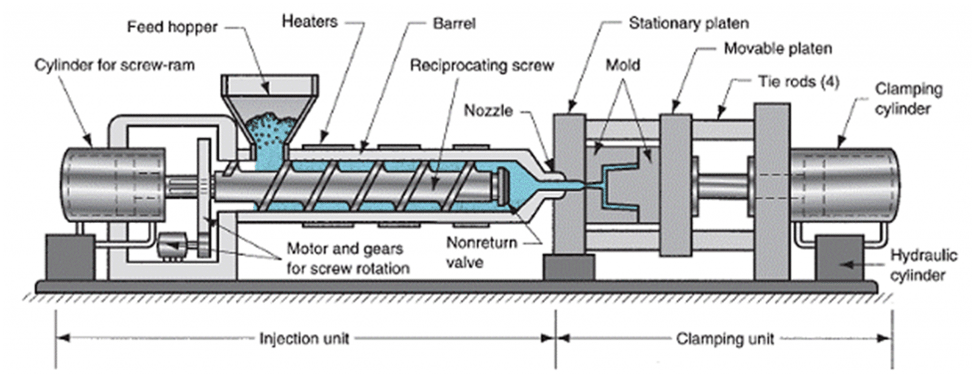
Injection Steps
Witness fast mold manufacturing (FMM) starting up which is the first step in the process of injection molding. To begin with, the pellets of plastic are fed from a hopper into the heating barrel and brought there, where they are heated to a temperature of 260 degrees Celsius. That’s where temperatures go up, and they are sufficient for the plastic to melt.
Additionally, the molten plastic is injected under high pressure into the mold cavity that the screw forces it. FMM facilitates an idea that enables reducing cycle times and therefore improving efficiency.
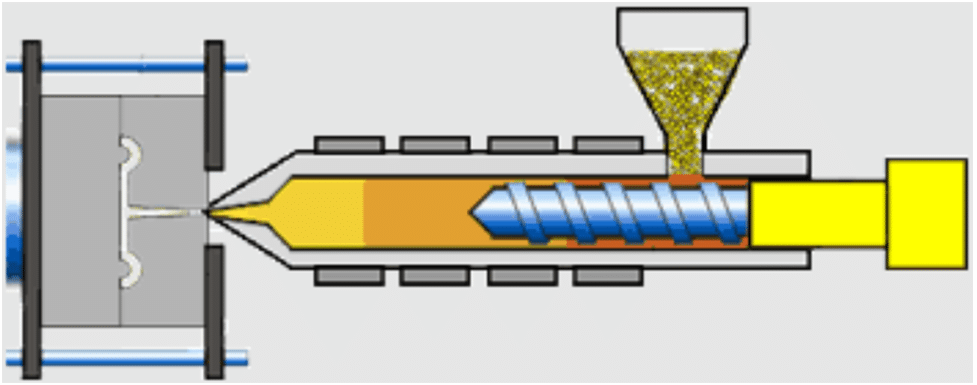
Resin Melting
3-D printing is a technology on the rise. It allows for the creation of complex shapes and it is a cost-effective process compared to other mold manufacturing techniques. The melting down begins by receiving resin pellets as the first input. Heat brings it to a melting point.
Temperatures rise and melt the pellets. The FMM processing line provides heating designed for the purpose of efficient and uniform melting. Eventually, this step is indispensable, to guarantee optimal flow and molding in cases of passivity production, which are the main requirements for better quality without wasting time. List of All Categories
Molding
The process of molding in fast mold manufacture, which is similar to injection molding, turns the viscous mass of liquid resin into refined and highly detailed parts. And upon the addition of resin to the form, as it cools and solidifies. As the mold opens, the pin is split out and the part is taken out. FMM’s cooling procedure uses advanced mechanisms that increase the output and can be accepted without affecting the standard.
| Aspect | Injection Molding Process | From Melting to Molding |
| Process Stages | Injection Steps | Resin Melting |
| Material Transformation | Resin Melting | – |
| Heat Application | Yes | Yes |
| Equipment Required | Injection Molding Machine | Melting Unit |
| Primary Function | Forming | Melting Polymer |
| Key Activities | Injecting, Cooling | Heating, Mixing |
Table on Injection Molding Process: From Melting to Molding!
Advanced Mold Types and Their Uses!
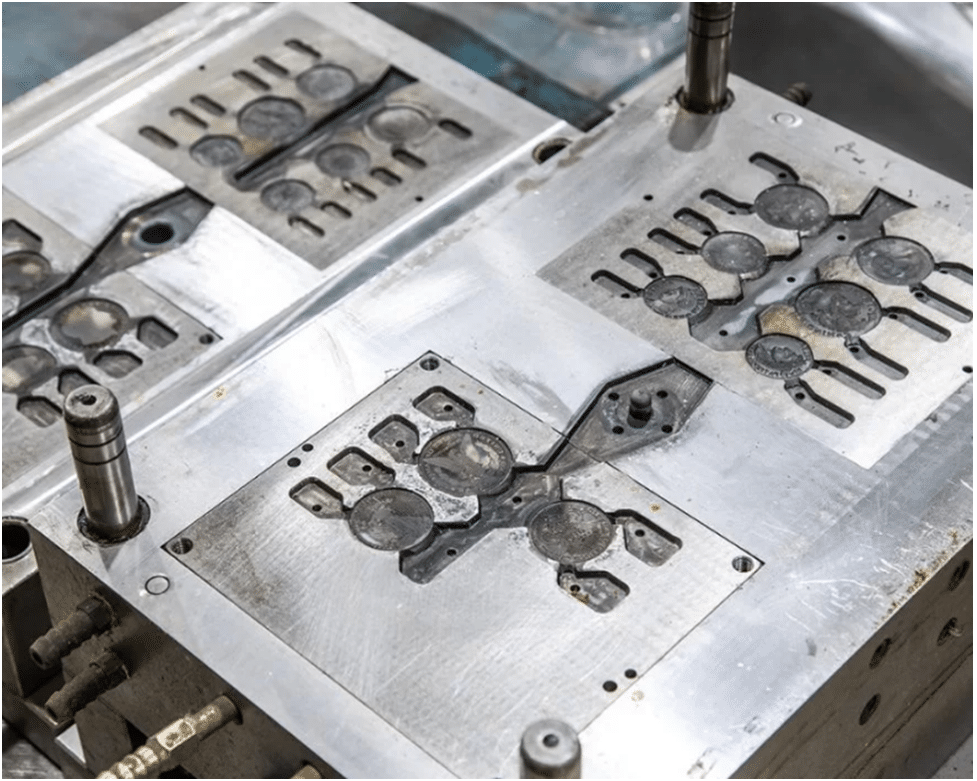
Mold Configurations
Fast mold manufacturing is very capable of simplifying the design and development process through the use of CAD and CAM systems. It supports various settings, including two-plate, three-plate, and stack molds. This will, in essence, hasten the prototyping processes, therefore enabling speedy development, so that a design can be improved, tried out and referred back to in the next stages. This area is particularly valuable in producing small batch sizes for such industries as automotive and consumer electronics.
Applications
With fast 3D printing cutting production time for prototypes, mold making is influencing precision and efficiency-driven sectors. They are of paramount importance i.e. dashboards and bumpers in the automotive industry, syringes in healthcare while in consumer goods, these are packaging solutions. This is done to achieve lead time reduction and this works well for companies looking to roll out their products to the market quickly.
Hot Runner Molds
Hot injection molds in rapid mold manufacturing allow for the proper flow of plastic thereby decreasing the plastic waste and mold cycles. The heated components inside were deployed to preserve the required melting temperature which in turn gave rise to faster production speed. This processing method without any doubt ensures the best-in-class production of bulk products where costs for time and materials count.
Insert Molds
Molding integration via this rapid manufacturing approach simultaneously enables the product features to be increased as different materials are brought into a single component.
It supplies materials processing of metal or other materials into plastic parts directly as a result increases the design possibility and the strength of the part. This is not only broadly applied in electronics to assemble metal pads and casing layers, but also used in industrial machinery fields, like mechanical arms.
Enhancing Mold Design with Ribs, Bosses, and Inserts!
Functionality Design
In quick mold manufacturing technology, user experiences – related functions design operates from the perspective of the experimental procedure. The fashion to integrate snaps and hinges into the products through the in-mold process provides an opportunity for the designers to design complex, multi-functional parts rapidly. This is possible through integration, which shortens or simplifies the course of assembly and gets the product ready for use.
Strength Considerations
Adding the right materials for all components of the mold prevents material input for slag or any other weaker materials. Strategic positioning of thick-end sections and stress transitions can reduce the aggressive stress effects. This provision provides that, apart from the normal use and wear, such parts should keep their integrity throughout time.
Ribs Incorporation
Ribs have an important role in the mold-making process, as a tool for making parts that in other cases would require too much bulk. They primarily act along lines, thus increasing flexural stiffness when properly placed. This way, the designers can achieve light-built constructions that do not limit the functionality of the structure but are cheap at the same time.
| Feature | Ribs | Bosses | Inserts |
| Functionality Design | Improves structural integrity and stiffness | Provides mounting points for components | Enhances mold versatility and customization |
| Strength Considerations | Reinforces critical areas against deformation | Increases load-bearing capacity | Reinforces specific regions prone to wear and tear |
| Ribs Incorporation | Integrates seamlessly into mold geometry | Offers additional support without sacrificing space | Facilitates easy installation and removal for maintenance |
Table on Enhancing Mold Design with Ribs, Bosses, and Inserts!
Conclusion
fast mold manufacturing gives a tech start-up the upper hand regarding speed and accuracy while relying on innovative tools for the increased portfolio. Do not stick to conventional ways. Instead, speculate on the area of potential improvement that can outpace competitors and meet rapid market shifts and demands.