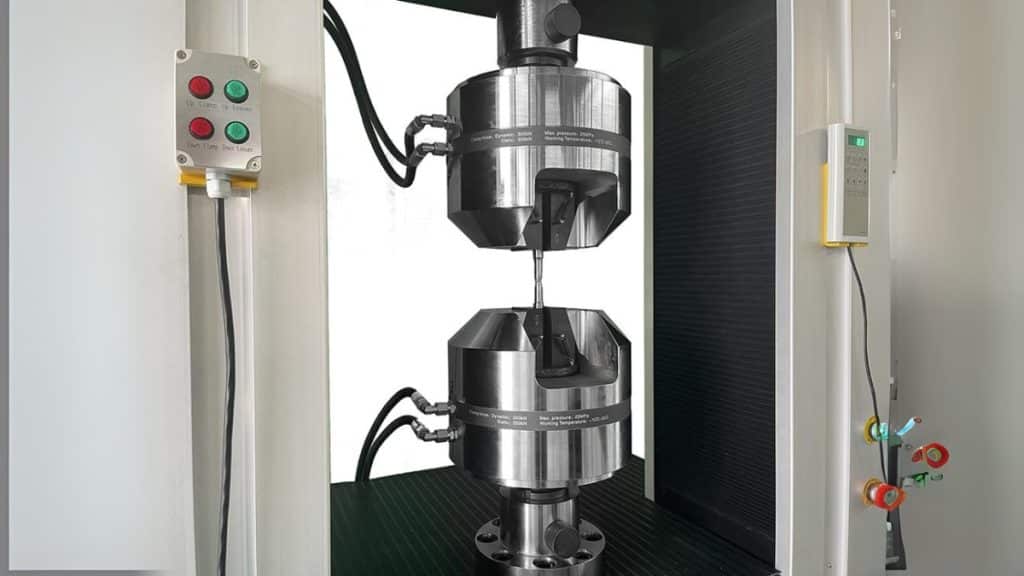
Military technology depends on materials that withstand extreme forces, high-impact conditions, and dynamically changing environments. From armored vehicles and aircraft frames to naval vessels and protective gear, every component must be built using alloys that offer superior strength, durability, and resistance to mechanical stress. Failure of these materials in critical situations can lead to catastrophic consequences, which is why the performance of these materials is a top priority for defense manufacturers.
Tensile testing is an essential step in verifying military-grade alloy reliability. By applying controlled tension to a material sample, engineers can evaluate tensile strength, yield strength, and ductility, determining how well an alloy can resist breaking under stress. These insights are crucial for designing alloys that meet and exceed modern military performance demands.
The purpose of this article is to explore why tensile testing is indispensable in military alloy development, how standardized testing protocols guarantee consistency, and the importance of high-precision tensile testing equipment in obtaining reliable results. Understanding these aspects is necessary for advancing next-generation military materials that improve safety, longevity, and overall operational effectiveness.
The Significance of Tensile Testing in Military Alloy Development
Military-grade alloys are engineered to meet strict performance standards so that they can endure combat conditions, high-stress loads, and long-term exposure to harsh environments. Unlike conventional materials, these alloys require precise mechanical property verification to function as intended in mission-critical applications. Tensile testing provides the data necessary to validate their strength, ductility, and overall durability, making it a key step in alloy development.
When an alloy is subjected to a tensile test, it undergoes controlled stretching until it reaches its failure point. This test measures:
- Ultimate tensile strength (UTS) – The maximum stress a material can withstand before breaking.
- Yield strength – The stress level at which a material permanently deforms.
- Elongation – The amount a material stretches before failure, indicating its ductility.
By analyzing these properties, military engineers can determine whether an alloy is suitable for applications like protective armor, high-speed aircraft, or submarine hulls. If an alloy fails to meet the necessary mechanical thresholds, adjustments can be made to its composition or heat treatment process to enhance its performance.
Strength and Toughness for Mission Success
One of the most critical factors in military alloys is their ability to balance strength and toughness. While a high-strength material can resist breaking under heavy loads, toughness makes certain that it can also absorb impact without sudden failure.
To cite one example, armor plating for military vehicles must withstand ballistic impacts while remaining structurally intact. Similarly, fighter jet components need high strength-to-weight ratios to maintain agility without sacrificing durability. Tensile testing allows engineers to fine-tune these alloys so that they provide optimal mechanical performance for each military application.
Beyond battlefield scenarios, military alloys must also endure environmental challenges such as saltwater corrosion, extreme temperatures, and repeated stress cycles. Tensile testing conducted under varied conditions helps determine how these materials respond to different operational environments, guiding the development of alloys with enhanced longevity and performance stability.
Standardized Testing Protocols and Their Relevance
Tensile testing in military alloy development is not just about assessing material performance—it’s about ensuring consistency, reliability, and compliance with strict military standards. Given the critical nature of defense applications, every alloy used in military vehicles, aircraft, and protective equipment must meet predefined mechanical property thresholds. To achieve this, manufacturers rely on internationally recognized testing protocols that provide uniform testing conditions and comparable results.
Achieving Consistency in Material Performance
Military-grade materials must perform consistently across manufacturing batches. Production variations could lead to unpredictable weaknesses, putting lives at risk in high-stress situations. Standardized tensile testing methods help eliminate these inconsistencies by ensuring that every test follows the same procedures, parameters, and evaluation criteria.
Among the most widely used standards for tensile testing of military alloys are:
- ASTM E8/E8M – The standard method for tensile testing of metallic materials, resulting in reliable data on strength and ductility.
- ISO 6892 – A global standard outlining test conditions, specimen preparation, and data analysis for metallic materials under tensile load.
- MIL-STD specifications – Military-specific testing guidelines that define performance expectations for defense materials.
Improving Reliability Through Rigorous Testing
In military applications, materials must withstand extreme stress without failure. Whether in aircraft subjected to rapid pressure changes, naval vessels facing corrosive seawater, or armored vehicles absorbing high-impact forces, alloy mechanical integrity determines mission success or failure.
Tensile testing under varied conditions, including high and low temperatures, cyclic loading, and exposure to corrosive elements, helps guarantee that materials maintain performance over time. This data enables military engineers to make critical decisions about material selection, preventing structural weaknesses that could compromise safety and operational effectiveness.
Optimizing Military Alloy Properties with Advanced Testing Methods
Beyond standard tensile testing, advanced testing methods provide deeper insights into how military alloys respond to stress. Modern testing facilities use specialized testing techniques to replicate real-world military conditions, assuring that alloys meet the strictest durability and reliability requirements.
Simulating Real-World Military Conditions
For optimum performance of an alloy’s performance in combat and harsh operational environments, advanced tensile testing includes additional stress factors, such as:
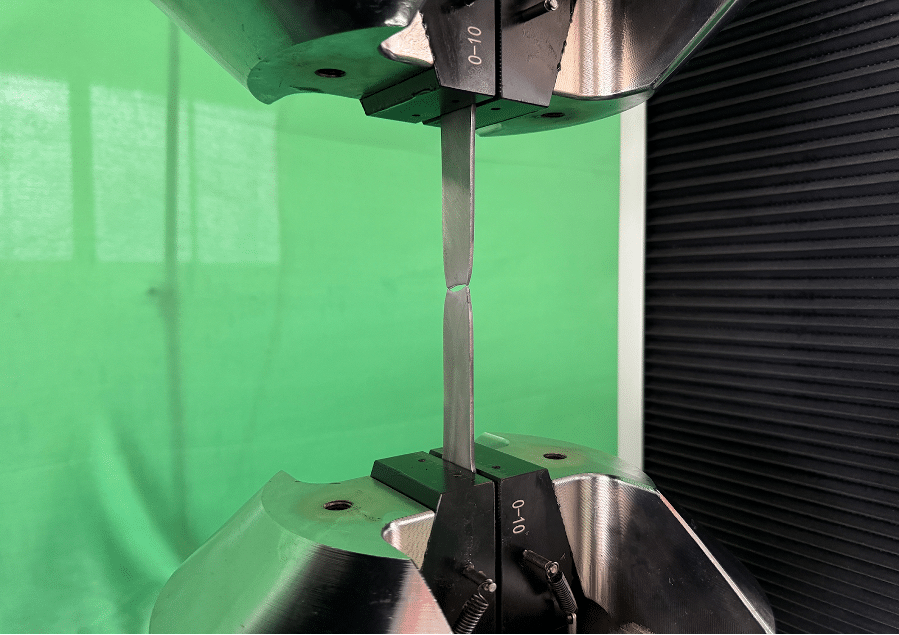
- High-strain rate testing – Simulates extreme forces experienced in ballistic impacts or explosive events.
- Fatigue testing – Measures how repeated stress cycles affect material performance over time.
- Environmental testing – Evaluate an alloy’s ability to resist corrosion, oxidation, and temperature fluctuations.
Contribution of Data-Driven Alloy Development
Tensile testing doesn’t just confirm material properties—it guides military alloy development. By analyzing test results, engineers can adjust alloy compositions, fine-tune heat treatments, and optimize microstructures to achieve higher strength, improved toughness, and better resistance to failure.
It is through this iterative process that military alloys used in defense applications are engineered for peak performance and long-term durability, assuring that modern military technology is safe and effective.
How Advanced Equipment Achieves Accurate Testing Outcomes
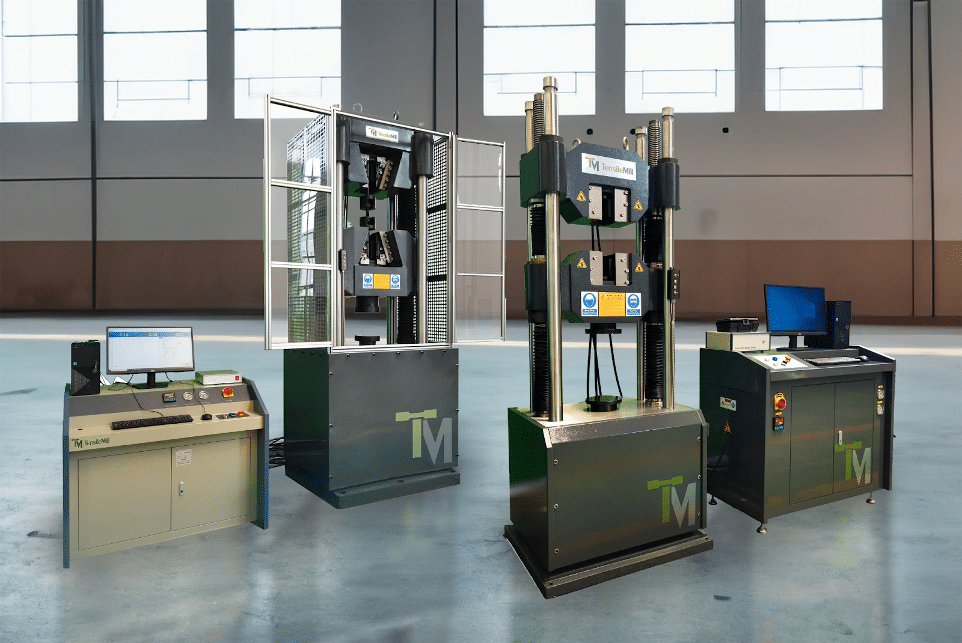

The accuracy and reliability of tensile testing results depend heavily on the quality of the equipment used. In military alloy development, precision is non-negotiable. Even minor alterations in test conditions can lead to misleading data and incorrect performance evaluations. That’s why military manufacturers and research facilities rely on state-of-the-art testing machines.
The Need for High-Precision Tensile Testing Machines
Modernuniversal testing machines (UTMs) handle high-strength, military-grade materials while maintaining precise force control, strain measurement, and data collection. These machines are equipped with:
- High-accuracy load cells that measure forces with minimal deviation.
- Advanced gripping systems that securely hold test specimens without premature failure.
- Digital extensometers that capture elongation and strain accurately.
The Necessity of Specimen Preparation Equipment
Accurate tensile testing starts with properly prepared specimens. Tensile specimen preparation machines, metallographic cutters, and precision grinding tools are required to make sure that test samples meet ASTM and ISO dimensional requirements.
If specimens have surface imperfections, misaligned edges, or incorrect dimensions, test results can be skewed, leading to unreliable data. High-precision sample preparation equipment provides uniformity, allowing for consistent and repeatable tensile testing among different material batches.
Investing in cutting-edge tensile testing machines and advanced specimen preparation tools ensures that military alloys are tested with the highest accuracy, supporting the development of stronger, more resilient defense materials.

Advancing Military Alloys Through Reliable Testing
Tensile testing is a key component of military alloy development, assuring that materials meet modern defense applications’ extreme performance demands. By assessing tensile strength, ductility, and durability, engineers can optimize alloy compositions, optimize structural resilience, and prevent material failures in mission-critical scenarios.
Standardized testing protocols and advanced testing methods provide highly accurate insights into material behavior, allowing manufacturers to refine alloys for maximum toughness, impact resistance, and long-term performance. However, the precision of these results depends on the quality of the tensile testing machines and specimen preparation equipment.
With high-tech testing systems, automated data collection, and precision-cut specimens, military engineers can develop alloys that exceed performance expectations, guaranteeing safety and reliability in combat and defense operations. Technological advances are enabling the creation of even stronger, more resilient military materials, supporting the next generation of defense innovation.
