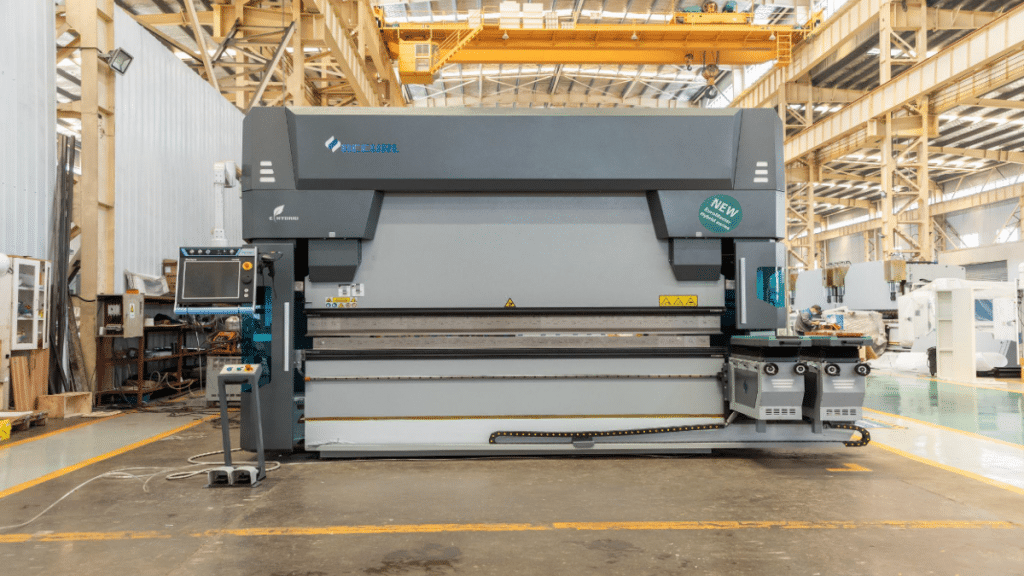
A press brake is a machine used in metal fabrication for bending sheet metal with high precision. It plays a vital role in modern manufacturing, enabling the creation of complex metal components for industries such as automotive, aerospace, and construction.
Press brake machines by ACCURL are renowned for their advanced technology and reliability, making them a top choice for precision bending tasks. Over the years, press brake technology has transformed significantly, with 2025 introducing smarter, more efficient bending solutions powered by AI and automation.
What Is a Press Brake and How Does It Work?
A press brake is a metal bending machine that shapes sheet metal by applying force through a punch and die system.
Core Components and Their Functions:
- Ram: The moving part applying force to the punch.
- Bed: The stationary base holding the die.
- Back Gauge: Guides the material for precise positioning.
- Punch and Die: The tools used for bending the sheet metal.
- Control Unit: Manages machine settings and automation.
The press brake works by lowering the ram with the punch onto the sheet metal placed on the die, bending the material to a desired angle.
What Are the Different Types of Press Brakes?
Different press brakes operate using varying mechanisms. Each type has unique advantages and drawbacks.
Mechanical Press Brakes
Uses a flywheel and clutch system for bending operations. Pros: Reliable for repetitive tasks, lower cost. Cons: Limited flexibility, slower adjustments.
Hydraulic Press Brakes
Uses hydraulic cylinders for force generation. Pros: Consistent pressure, suitable for thicker materials. Cons: Higher maintenance needs.
Pneumatic Press Brakes
Uses compressed air for bending. Pros: Faster operation, lower energy use. Cons: Lower force output, not suitable for heavy-duty tasks.
Servo-Electric Press Brakes
Electric motors drive the bending process. Pros: High precision, energy efficient. Cons: Limited force output for thicker materials.
Hybrid Press Brakes
Combines hydraulic and electric mechanisms. Pros: Energy efficient, versatile. Cons: Higher initial cost.
What Are the Key Components of a Modern Press Brake?
Key components that define modern press brakes:
- Ram: Delivers bending force.
- Bed: Supports the die and material.
- Punch and Die: Toolset for forming the material.
- Back Gauge System: Ensures precise material positioning.
- CNC Control Panel: Automates settings and adjustments.
- Safety Mechanisms: Prevent accidents during operation.
How Has Press Brake Technology Evolved?
Press brake technology has seen significant advancements:
- 1980s: Introduction of CNC controls.
- 1990s: Enhanced hydraulic systems.
- 2000s: Improved automation and servo-electric models.
- 2020s: IoT integration and smart sensors.
Key breakthroughs include:
- CNC integration for better accuracy.
- Real-time error detection.
- Energy-efficient hybrid systems.
- IoT connectivity for predictive maintenance.
What Are Smarter Bending Solutions in 2025?
The latest press brake innovations focus on smarter bending:
- AI Integration: Optimizes bending sequences.
- Real-time Error Detection: Prevents material waste.
- Automated Tool Changing: Enhances production speed.
- Energy Efficiency Improvements: Reduces power consumption.
What Are the Benefits of Modern Press Brakes?
- Higher Precision: Consistent bends with minimal error.
- Increased Productivity: Faster cycle times and automation.
- Reduced Material Waste: Real-time error detection.
- Improved Operator Safety: Advanced safety mechanisms.
What Types of Materials Can a Press Brake Bend?
- Mild Steel: Common for construction and machinery.
- Stainless Steel: Resistant to corrosion.
- Aluminum: Lightweight and corrosion-resistant.
- Copper: Conductive and malleable.
- Titanium: Strong and lightweight for aerospace use.
How to Choose the Right Press Brake for Your Needs?

Key factors to consider:
- Material Thickness: Determines required tonnage.
- Bending Capacity: Maximum length the machine can handle.
- Automation Level: CNC and AI integration options.
- Safety Features: Built-in systems for operator protection.
What Are the Main Parameters for Accurate Bending?
- Tonnage: Force required for bending.
- Bend Angle: Desired angle of the bend.
- Bend Radius: Radius inside the bend.
- Material Springback: Tendency of metal to return to its original shape.
What Are Common Bending Techniques?
- Air Bending: Minimal contact with the material.
- Bottom Bending: Material fully contacts the die.
- Coining: Full compression for precise bends.
How Does CNC Control Impact Press Brake Performance?
- Enhanced Precision: Accurate bends with minimal error.
- Complex Bends Simplified: Pre-programmed patterns.
- Reduced Setup Time: Faster adjustments and programming.
What Are the Key Safety Features of Modern Press Brakes?
- Laser Safety Systems: Detects hand placement.
- Light Curtains: Stops machine if obstruction occurs.
- Two-Hand Controls: Requires both hands to operate, preventing accidental activation.
What Industries Benefit Most from Modern Press Brakes?
- Automotive: Frame components and panels.
- Aerospace: Aircraft panels and brackets.
- Construction: Beams and panels.
- Electronics: Enclosures and precision panels.
How to Maintain a Press Brake for Optimal Performance?
- Regular Lubrication: Prevents wear and tear.
- Tool Inspection: Ensures sharp and intact tools.
- Calibration Checks: Maintains accuracy over time.
What Are Common Mistakes When Using a Press Brake?
- Incorrect Tonnage Calculation: Leads to improper bends.
- Improper Tooling Selection: Reduces precision.
- Skipping Maintenance: Leads to machine failure.
What Are the Costs Associated with Press Brake Technology?
What Are the Operating Costs?
- Energy consumption.
- Maintenance and calibration.
- Operator training.
What Are the Alternatives to Press Brakes for Metal Bending?
- Roll Bending: For cylindrical bends.
- Folding Machines: Suitable for sheet metal folding.
- Panel Benders: Ideal for high-volume panel production.
How to Implement Press Brake Automation in 2025?
- Collaborative Robots (Cobots): Assist operators with loading.
- Automated Loading Systems: Reduce manual labor.
- Smart Sensor Integration: Real-time monitoring and adjustments.
Conclusion
Press brake technology has come a long way, with 2025 marking a significant leap in smarter bending solutions. Innovations like AI integration, real-time error detection, and automation are revolutionizing metal fabrication, making it safer, faster, and more efficient. Embracing these advancements is key for manufacturers seeking precision, productivity, and sustainability.
