Although weight loss is often seen as a simple math problem — calories in vs. calories out, it is much more complicated. Diet and exercise are important, but often, another key that is missed is the role hormones play in weight loss. The body’s chemical messengers, known as hormones, control your appetite, metabolism, fat storage, and even how you respond to exercise. Knowing how these hormones work can help you determine how to use your weight loss tactics to achieve long-term success.
Impact of Hormones on Weight Loss
Let’s explore key hormones and their impact on your weight loss journey!
1. Leptin
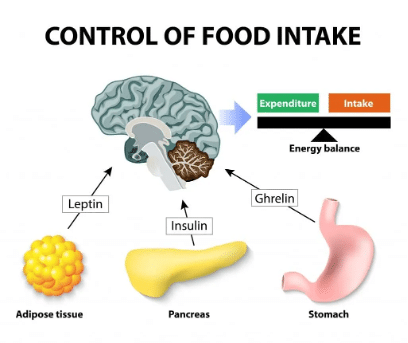
Leptin is called the ‘satiety hormone’. It is produced by fat cells and tells your brain that you have had enough and are full, keeping you away from taking in too much food.
Impact on Weight Loss: If leptin is working properly, it helps to reduce the appetite and prevents overeating. But in the case of leptin resistance, associated with overeating and obesity, the brain stops responding to these signals and leads to weight gain. Proper diet and sleep can improve leptin sensitivity and enhance weight loss efforts.
2. Insulin
Pancreas makes insulin in your body and it plays a crucial role in maintaining and regulating blood sugar levels. It allows cells to absorb glucose from the bloodstream and store excess glucose as fat.
Impact on Weight Loss: If you have high insulin levels, it will cause fat storage around your abdomen. An elevated insulin level may be due to eating more carbs or your body’s resistance to using insulin, making it more difficult for your body to burn fat. Balanced meals and avoiding sugar spikes will help you manage insulin and achieve significant weight loss.
3. Ghrelin
Ghrelin is the ‘hunger hormone’ produced in the stomach. It sends hunger signals to the brain and stimulates appetite.
Impact on Weight Loss: Ghrelin levels are high before meals, and low after meals. However, during weight loss the level of ghrelin rises, making you feel hungrier. Opt for portion control, protein rich and healthier foods, and practice mindful eating will help control your ghrelin levels, lowering appetite and promoting weight loss.
4. Thyroid Hormones (T3 & T4)
The thyroid gland produces thyroid hormones that control everything from your metabolism rates to heart rates and our body temperature. T3 (triiodothyronine) and T4 (thyroxine) tell your body when to burn food for energy.
Impact on Weight Loss: It makes weight loss harder if you have an underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism). Symptoms of hypothyroidism include fatigue, weight gain and cold intolerance. Proper nutrition, iodine intake, as well as support from medical doctors may be used to normalize thyroid function while losing weight.
5. Cortisol
The adrenal glands produce this stress hormone called cortisol, managing your stress and playing an important role in fat storage and metabolism.
Impact on Weight Loss: When cortisol levels are chronically elevated as a result of prolonged stress, it will lead to increased appetite and fat storage in the abdominal area. Stress management via yoga, meditation, or simply getting enough sleep can lower cortisol levels and promote weight loss.
6. Estrogen
Estrogen is a female sex hormone and is important for your reproductive health. It also plays a role in fat storage.
Impact on Weight Loss: Women have an ongoing change in the levels of estrogen with age, and most particularly so during the time of menopause. Loss of estrogen, in fact, causes belly fat. Diet, exercise, even hormone replacement therapy (HRT) can help you strike a proper balance of estrogen and maintain weight.
7. Testosterone
Testosterone is an important male sex hormone, playing a role in muscle mass and fat distribution in both men and women.
Impact on Weight Loss: Lower testosterone levels cause less muscle mass loss and more fat storage, which makes weight loss harder. Good strength training, enough sleep, and a protein rich diet can raise testosterone levels, that aid in fat loss, and muscle growth.
Ways to Balance Hormones for Weight Loss Success
You can balance your hormone levels and make your medical weight loss program effective by following these points:
1. Exercise Regularly
Strength training and high intensity interval training (HIIT) can help balance cortisol and enhance testosterone. Exercise also enhances insulin sensitivity and stimulates the production of hormones which encourage fat loss.
2. Adopt a Balanced Diet
Eat whole foods that are full of fiber, lean proteins, and healthy fat to balance your insulin and leptin levels. Avoid processed food, sugars, and refined carbohydrates to reduce insulin spikes and improve satiety.
3. Manage Stress
Chronic stress level increases the level of cortisol and leads you towards weight gain. Practice stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga to lower stress levels and assist in weight loss.
4. Get Enough Sleep
Sleep deprivation increases ghrelin levels and lowers leptin levels, increasing cravings and overeating. Get 7-9 hours of good quality sleep every night to balance your hormones and promote weight loss.
5. Seek Help from your Healthcare Professional
If you think hormonal imbalances are stopping you from losing weight, seek medical help. Consult your doctor to evaluate polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), insulin resistance, or thyroid disorders, as these conditions require medical interventions
Conclusion
Weight loss is heavily dependent on hormones as they are responsible for everything from hunger to fat storage, metabolism, and energy levels. If you know how hormones like insulin, leptin, ghrelin, cortisol, and thyroid hormones function in your body, you can better customize your approach to weight loss. So, focus on your balanced diet, regular exercise, stress management, and adequate sleep to keep your hormones in check and achieve sustainable weight loss with a provider on Klarity Health.
