“🔎Explore bladder cancer: recognise early symptoms 🚨, check out the latest treatment options 💊, and learn the ways of prevention 🛡️. Stay informed, stay healthy! 💪”
Bladder cancer is a serious condition that develops in the bladder’s inner lining, often manifesting through symptoms such as blood in the urine, frequent urination, and pain. Factors such as smoking and chemical exposure significantly increase the risk of developing this disease. By understanding the bladder cancer symptoms, treatment options, and preventive measures, individuals can take proactive steps toward early detection and improved outcomes.
Understanding Bladder Cancer Matters
Comprehending bladder cancer’s symptoms, treatment pathways, and preventive strategies is crucial for improving treatment success, reducing the likelihood of developing the condition, and ensuring informed decision-making for those at risk or affected by the disease.
What is Bladder Cancer?
Bladder cancer is characterised by abnormal cell growth within the bladder’s lining. This condition often results in symptoms like painful urination, blood in the urine, and bladder discomfort. Diagnosis typically requires medical imaging, urine tests, and biopsy to assess the presence and extent of cancerous growths. Bladder cancer rates vary globally, with the highest incidences found in North America and Europe. Awareness and proactive health management are key to improving survival rates and enhancing treatment outcomes.
Risk Factors for Bladder Cancer
Several factors heighten the likelihood of developing bladder cancer. Smoking is the most significant risk factor, doubling the chances of developing bladder cancer. Exposure to certain industrial chemicals used in manufacturing and dye production increases risk. Chronic bladder infections, long-term bladder irritation, or inflammation can heighten susceptibility. Bladder cancer is more prevalent in individuals over 55 and is diagnosed more frequently in men than women. Those with a family history of bladder cancer may have a heightened genetic predisposition.
Identifying Symptoms of Bladder Cancer
Early symptoms of bladder cancer may include blood in the urine, frequent urination or urgency, and pain or burning during urination. As the cancer advances, symptoms may intensify to include pelvic pain, back pain, and unexplained weight loss.
The Importance of Early Detection
Early detection can significantly improve bladder cancer outcomes. Timely diagnosis allows for less aggressive treatment options and a higher likelihood of successful management. Regular screenings, especially for those at higher risk, can help identify bladder cancer in its earliest stages when intervention is most effective.
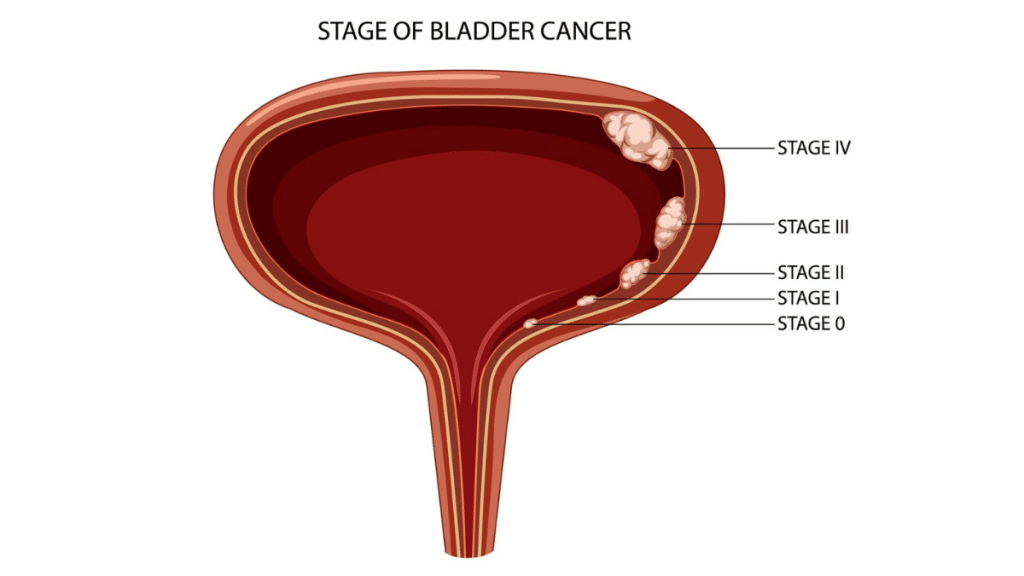
Detailed Explanation of Bladder Cancer Stages
Bladder cancer is categorised into several stages based on tumour size, depth, and spread. Stage 0 refers to cancer cells confined to the bladder’s inner lining. Stage I indicates cancer has spread slightly deeper but remains within the bladder. Stage II involves cancer invading the bladder’s muscle wall. Stage III describes cancer that has spread to nearby tissues or lymph nodes. Stage IV is the most advanced stage, with cancer spreading to distant organs such as the lungs or bones. Understanding these stages is crucial for determining treatment approaches and predicting patient outcomes.
Treatment Options for Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer treatments vary based on the stage and overall patient health. Surgery is often used to remove tumours in early-stage cases or to remove the bladder in severe conditions. Chemotherapy may be administered before or after surgery to kill remaining cancer cells. Immunotherapy boosts the immune system’s ability to target and destroy cancer cells. Radiation therapy is often used alongside other treatments to target localised cancer cells. Post-treatment care is essential to monitor recovery, manage side effects, and prevent recurrence.
Prevention Strategies for Bladder Cancer
Adopting healthy habits can significantly reduce bladder cancer risks. Avoiding tobacco use, maintaining a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables, and staying hydrated to help flush harmful toxins from the bladder are effective strategies. Routine health screenings can detect bladder cancer early, improving treatment outcomes. Individuals at higher risk should schedule frequent check-ups with their healthcare provider. Those with a family history of bladder cancer should consider genetic screening to assess their risk and adopt preventive measures accordingly.
Importance of Awareness
Raising awareness about bladder cancer promotes early detection and encourages individuals to prioritise their health. Educational campaigns, support groups, and healthcare initiatives can help communities stay informed and proactive.
Conclusion
Bladder cancer is a serious condition that requires awareness, early detection, and informed decision-making. By recognising symptoms, understanding treatment options, and adopting preventive strategies, individuals can take proactive steps toward safeguarding their health. Regular check-ups and healthy lifestyle choices remain pivotal in the fight against bladder cancer.